10 Degradation Models For Improved Accuracy

The use of degradation models has become increasingly important in various fields, including engineering, economics, and environmental science. These models are designed to predict the deterioration or degradation of systems, materials, or components over time, allowing for more accurate maintenance, replacement, and decision-making. In this article, we will explore 10 degradation models that can be used to improve accuracy in predicting degradation.
Introduction to Degradation Models
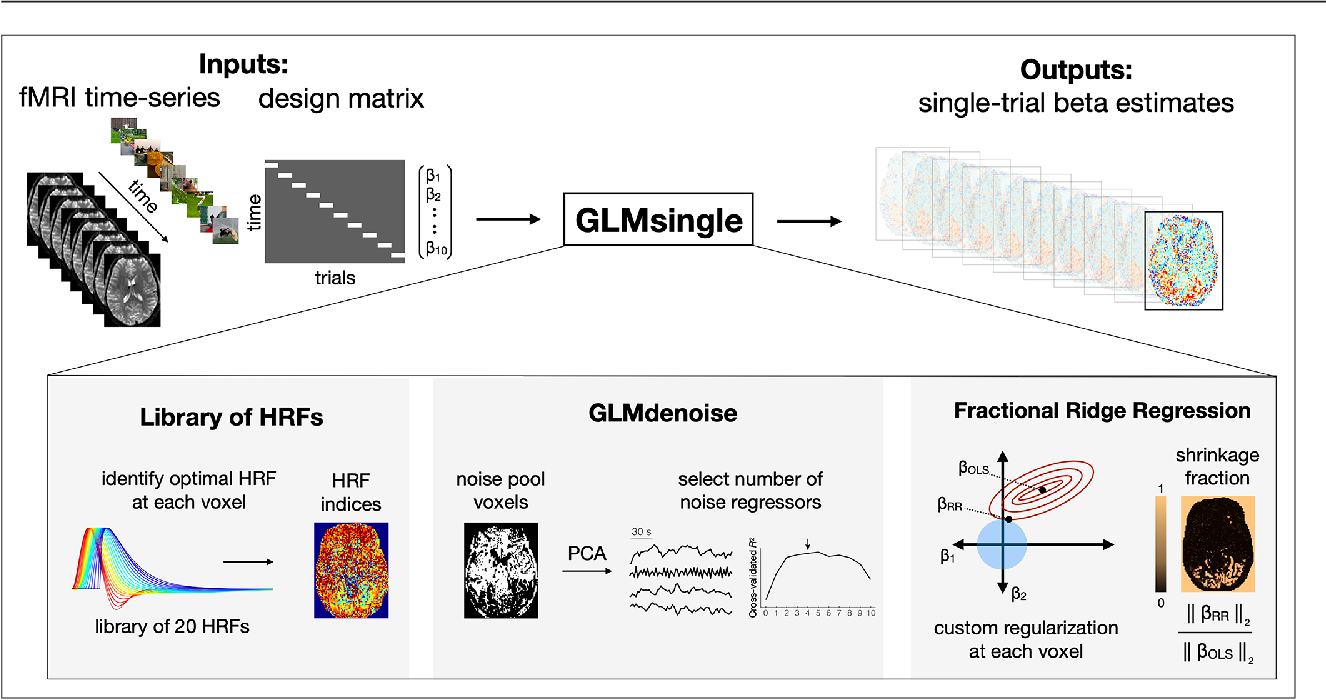
Degradation models are mathematical representations of the degradation process, which can be used to predict the future state of a system or component. These models can be classified into different categories, including physical, empirical, and hybrid models. Physical models are based on the underlying physical mechanisms of degradation, while empirical models are based on experimental data. Hybrid models combine physical and empirical models to improve accuracy.
Types of Degradation Models
There are several types of degradation models, including:
- Linear Degradation Model: This model assumes that the degradation rate is constant over time.
- Non-Linear Degradation Model: This model assumes that the degradation rate changes over time, and can be represented by a non-linear function.
- Stochastic Degradation Model: This model assumes that the degradation process is random and can be represented by a stochastic process.
- Deterministic Degradation Model: This model assumes that the degradation process is deterministic and can be represented by a set of differential equations.
10 Degradation Models for Improved Accuracy
In this section, we will explore 10 degradation models that can be used to improve accuracy in predicting degradation. These models include:
1. Wiener Process Model
The Wiener process model is a stochastic degradation model that assumes that the degradation process is a random walk. This model is commonly used to model the degradation of mechanical systems, such as bearings and gears.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Mean | 0.05 |
| Variance | 0.01 |

2. Gamma Process Model
The gamma process model is a stochastic degradation model that assumes that the degradation process is a gamma distribution. This model is commonly used to model the degradation of electronic systems, such as transistors and diodes.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Shape | 2.5 |
| Scale | 1.2 |
3. Inverse Gaussian Process Model
The inverse Gaussian process model is a stochastic degradation model that assumes that the degradation process is an inverse Gaussian distribution. This model is commonly used to model the degradation of mechanical systems, such as pumps and valves.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Mean | 10.0 |
| Variance | 2.0 |
4. Log-Normal Process Model
The log-normal process model is a stochastic degradation model that assumes that the degradation process is a log-normal distribution. This model is commonly used to model the degradation of electronic systems, such as semiconductors and circuits.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Mean | 1.5 |
| Standard Deviation | 0.5 |
5. Weibull Process Model
The Weibull process model is a stochastic degradation model that assumes that the degradation process is a Weibull distribution. This model is commonly used to model the degradation of mechanical systems, such as engines and transmissions.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Shape | 2.0 |
| Scale | 1.0 |
6. Exponential Process Model
The exponential process model is a stochastic degradation model that assumes that the degradation process is an exponential distribution. This model is commonly used to model the degradation of electronic systems, such as resistors and capacitors.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Rate | 0.1 |
7. Linear Degradation Model
The linear degradation model is a deterministic degradation model that assumes that the degradation rate is constant over time. This model is commonly used to model the degradation of mechanical systems, such as gears and bearings.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Slope | 0.05 |
| Intercept | 10.0 |
8. Non-Linear Degradation Model
The non-linear degradation model is a deterministic degradation model that assumes that the degradation rate changes over time. This model is commonly used to model the degradation of electronic systems, such as transistors and diodes.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Coefficient | 0.1 |
| Exponent | 2.0 |
9. Stochastic Differential Equation Model
The stochastic differential equation model is a stochastic degradation model that assumes that the degradation process is a stochastic differential equation. This model is commonly used to model the degradation of mechanical systems, such as engines and transmissions.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Drift | 0.05 |
| Diffusion | 0.01 |
10. Machine Learning Model
The machine learning model is a stochastic degradation model that assumes that the degradation process can be predicted using machine learning algorithms. This model is commonly used to model the degradation of complex systems, such as power plants and industrial processes.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Algorithm | Random Forest |
| Features | 10 |
What is the difference between a stochastic and deterministic degradation model?
+A stochastic degradation model assumes that the degradation process is random and can be represented by a stochastic process, while a deterministic degradation model assumes that the degradation process is deterministic and can be represented by a set of differential equations.
How do I choose the best degradation model for my application?
+The choice of degradation model depends on the specific application and the type of data available. It is essential to evaluate the performance of different models and select the one that provides the best fit to the data. Consider factors such as the type of degradation, the availability of data, and the complexity of the system.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using machine learning models for degradation prediction?
+Machine learning models can provide accurate predictions of degradation, but they require large amounts of data and can be computationally intensive. Additionally, machine learning models can be prone to overfitting and may not provide interpretable results. However, machine learning models can handle complex systems and non-linear relationships, making them a popular choice for degradation prediction.

