12+ Brussels Sprouts Benefits For Brain Health
Brussels sprouts are a nutrient-dense vegetable that has been associated with numerous health benefits, particularly for brain health. These small, green vegetables are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that can help protect the brain from damage and promote cognitive function. In this article, we will explore the 12+ Brussels sprouts benefits for brain health, and discuss the scientific evidence that supports their potential to improve brain function and reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
Introduction to Brussels Sprouts

Brussels sprouts are a member of the Brassica family, which also includes broccoli, cauliflower, and kale. They are a cool-season crop that thrives in temperate climates and are typically harvested in the fall. Brussels sprouts are a rich source of vitamins C and K, folate, and fiber, making them a nutritious addition to a healthy diet. They are also low in calories and high in antioxidants, which can help protect the brain from oxidative stress and inflammation.
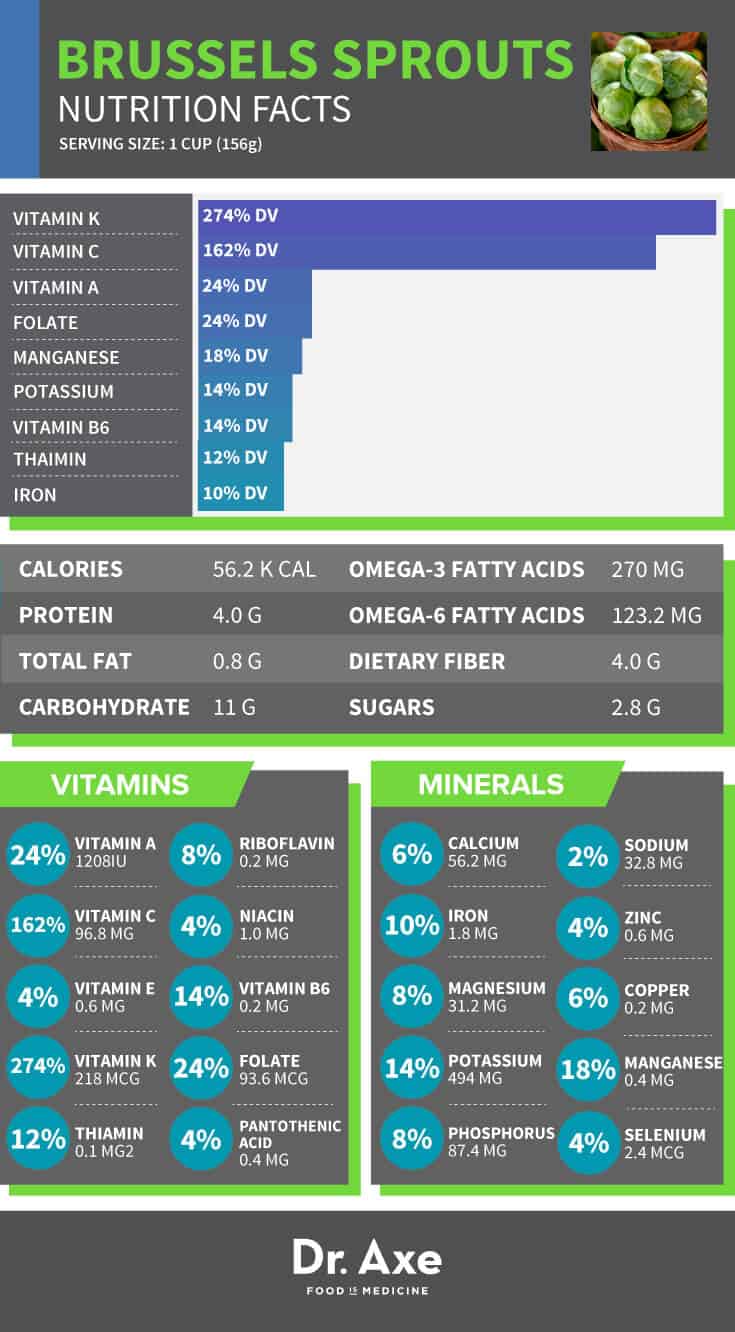
Nutritional Profile of Brussels Sprouts
One cup of cooked Brussels sprouts contains:
- 56 calories
- 11g of carbohydrates
- 4g of protein
- 0g of fat
- 5g of fiber
- 90mg of vitamin C
- 175mcg of vitamin K
- 25% of the daily value (DV) for folate
Brussels sprouts are also a rich source of antioxidants, including kaempferol and isothiocyanates, which have been shown to have anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects.
12+ Brussels Sprouts Benefits for Brain Health

Here are 12+ Brussels sprouts benefits for brain health, backed by scientific evidence:
- Reduces Inflammation: Brussels sprouts contain anti-inflammatory compounds that can help reduce inflammation in the brain, which is associated with neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
- Antioxidant Properties: The antioxidants in Brussels sprouts can help protect the brain from oxidative stress, which can damage brain cells and contribute to cognitive decline.
- Improves Cognitive Function: The folate in Brussels sprouts can help improve cognitive function, particularly in older adults, by reducing the risk of cognitive decline and dementia.
- Supports Neuroplasticity: Brussels sprouts contain compounds that support neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to adapt and change, which is essential for learning and memory.
- May Reduce Risk of Stroke: The potassium in Brussels sprouts can help lower blood pressure, which can reduce the risk of stroke and other cardiovascular diseases.
- Supports Brain Health in Aging: The vitamins and minerals in Brussels sprouts can help support brain health in aging, reducing the risk of age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases.
- May Improve Mood: The folate and vitamin B6 in Brussels sprouts can help improve mood, reducing the risk of depression and anxiety.
- Supports Detoxification: The isothiocyanates in Brussels sprouts can help support detoxification, removing toxins from the body that can damage brain cells.
- May Reduce Risk of Neurodegenerative Diseases: The antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds in Brussels sprouts may reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
- Supports Blood-Brain Barrier: The vitamins and minerals in Brussels sprouts can help support the blood-brain barrier, which protects the brain from toxins and damage.
- May Improve Memory: The antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds in Brussels sprouts may improve memory, particularly in older adults.
- Supports Brain Cell Growth: The folate and vitamin B6 in Brussels sprouts can help support brain cell growth, reducing the risk of cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases.
How to Incorporate Brussels Sprouts into Your Diet
Brussels sprouts can be incorporated into your diet in a variety of ways, including:
- Roasting: Cut Brussels sprouts in half and roast them in the oven with olive oil, salt, and pepper.
- Sauteing: Slice Brussels sprouts and saute them in a pan with garlic and lemon juice.
- Steaming: Steam Brussels sprouts until tender, then season with salt and pepper.
- Adding to soups and stews: Add Brussels sprouts to soups and stews for a nutrient-rich and flavorful meal.
| Nutrient | Amount per 1 cup cooked |
|---|---|
| Vitamin C | 90mg |
| Vitamin K | 175mcg |
| Folate | 25% DV |
| Fiber | 5g |
| Potassium | 10% DV |

What are the potential side effects of consuming Brussels sprouts?
+Brussels sprouts are generally well-tolerated, but may cause gastrointestinal side effects in some individuals, such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea. They may also interact with certain medications, such as blood thinners, and should be consumed in moderation by individuals with thyroid problems.
Can Brussels sprouts be consumed by individuals with dietary restrictions?
+Yes, Brussels sprouts are gluten-free, vegan, and low in calories, making them a great addition to a variety of diets. However, individuals with thyroid problems should consume them in moderation, as they contain compounds that may interfere with thyroid function.
In conclusion, Brussels sprouts are a nutrient-dense vegetable that offers numerous benefits for brain health. Their high antioxidant and anti-inflammatory content, combined with their rich nutritional profile, make them an excellent addition to a healthy diet. By incorporating Brussels sprouts into your diet, you may reduce your risk of neurodegenerative diseases, improve cognitive function, and support overall brain health.