12 Decimal Conversion Tips Easily

Converting between different number systems, especially decimal to other bases, is a fundamental skill in mathematics and computer science. Decimal, or base 10, is the most commonly used number system in everyday life, while other bases like binary (base 2), hexadecimal (base 16), and octal (base 8) are crucial in programming and computer operations. Mastering decimal conversion can enhance your understanding and proficiency in these fields. Here are 12 tips to easily convert decimals to other number systems and vice versa.
Understanding Number Systems

Before diving into conversion tips, it’s essential to understand the basics of different number systems. The decimal system, as mentioned, is base 10, using digits 0-9. The binary system is base 2, using only 0 and 1. Hexadecimal is base 16, utilizing digits 0-9 and letters A-F to represent numbers 10-15. Octal, or base 8, uses digits 0-7. Each system has its unique conversion method, but understanding the base is key to successful conversion.
Decimal to Binary Conversion
Converting decimal to binary involves dividing the decimal number by 2 and noting the remainder until the quotient is 0. The remainders, read from bottom to top, give the binary representation. For example, to convert 12 to binary: 12 divided by 2 is 6 remainder 0, 6 divided by 2 is 3 remainder 0, 3 divided by 2 is 1 remainder 1, and 1 divided by 2 is 0 remainder 1. Thus, 12 in binary is 1100.
| Decimal | Binary |
|---|---|
| 10 | 1010 |
| 12 | 1100 |
| 15 | 1111 |

Decimal to Hexadecimal Conversion
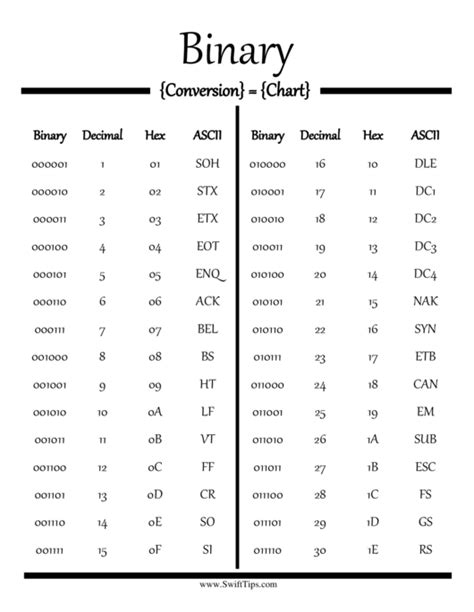
Converting decimal to hexadecimal can be done by continuously dividing the decimal number by 16 and noting the remainders. Each remainder corresponds to a hexadecimal digit (0-9, A-F). For example, converting 255 to hexadecimal: 255 divided by 16 is 15 remainder 15. Since 15 corresponds to F in hexadecimal, 255 is FF in hexadecimal.
Decimal to Octal Conversion
Converting decimal to octal involves dividing the decimal number by 8 and noting the remainders until the quotient is 0. The remainders, read from bottom to top, give the octal representation. For instance, to convert 12 to octal: 12 divided by 8 is 1 remainder 4, and 1 divided by 8 is 0 remainder 1. Thus, 12 in octal is 14.
| Decimal | Octal |
|---|---|
| 8 | 10 |
| 12 | 14 |
| 16 | 20 |
Converting Other Bases to Decimal

Converting from binary, hexadecimal, or octal to decimal involves multiplying each digit by the base raised to the power of its position, counting from right to left and starting at 0. For binary and octal, this is straightforward. For hexadecimal, remember that A=10, B=11, C=12, D=13, E=14, and F=15.
Binary to Decimal Example
Converting 1101 from binary to decimal: (1*2^3) + (1*2^2) + (0*2^1) + (1*2^0) = 8 + 4 + 0 + 1 = 13.
Hexadecimal to Decimal Example
Converting FF from hexadecimal to decimal: (15*16^1) + (15*16^0) = 240 + 15 = 255.
| Binary | Decimal |
|---|---|
| 1010 | 10 |
| 1101 | 13 |
| 1111 | 15 |
What is the easiest way to convert decimal to binary?
+The easiest way to convert decimal to binary is by using the division method, where you divide the decimal number by 2 and note the remainder until the quotient is 0. The remainders, read from bottom to top, give the binary representation.
How do I convert hexadecimal to decimal?
+To convert hexadecimal to decimal, multiply each hexadecimal digit by 16 raised to the power of its position, counting from right to left and starting at 0. Remember, A=10, B=11, C=12, D=13, E=14, and F=15.
Mastering decimal conversion enhances one’s ability to work with different number systems, a crucial skill in computer science and programming. By understanding the base of each system and applying the conversion methods, one can easily switch between decimal, binary, hexadecimal, and octal. Whether for academic purposes, professional development, or personal projects, proficiency in number system conversions is a valuable asset in today’s digital world.