36 Celsius To Fahrenheit Conversion Made Easy
The conversion of temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit is a common task in various fields, including science, engineering, and everyday life. One such conversion that is often required is 36 Celsius to Fahrenheit. In this article, we will explore the process of converting 36 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit, and provide a detailed understanding of the temperature scales and their applications.
Understanding the Celsius and Fahrenheit Scales

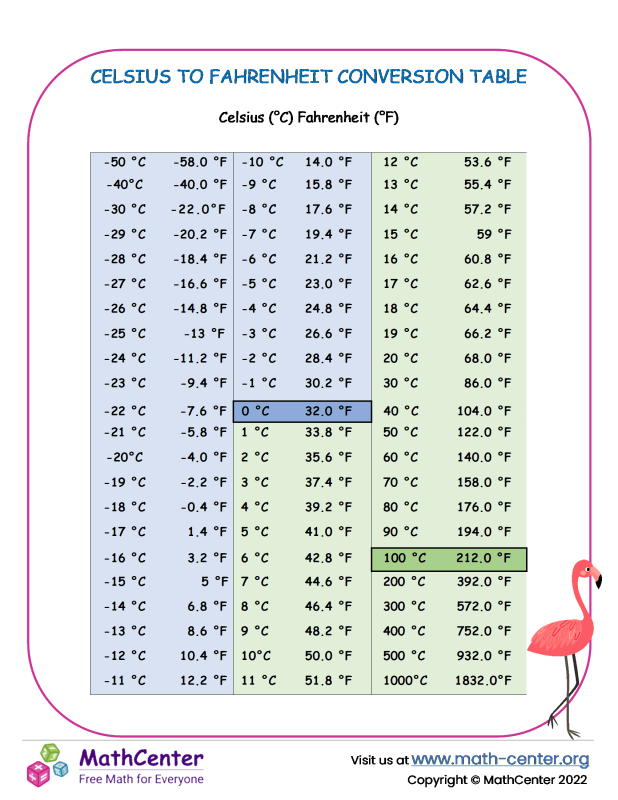
The Celsius scale and the Fahrenheit scale are two different temperature scales that are used to measure temperature. The Celsius scale is also known as the centigrade scale, and it is defined such that 0 degrees Celsius is the freezing point of water, and 100 degrees Celsius is the boiling point of water. On the other hand, the Fahrenheit scale is defined such that 32 degrees Fahrenheit is the freezing point of water, and 212 degrees Fahrenheit is the boiling point of water.
Conversion Formula
To convert a temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit, we can use the following formula: Fahrenheit = (Celsius * 9⁄5) + 32. This formula can be applied to any temperature in Celsius to obtain the equivalent temperature in Fahrenheit. For example, to convert 36 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit, we can plug in the value of Celsius as 36 in the formula and calculate the result.
The calculation would be: Fahrenheit = (36 * 9/5) + 32 = (324/5) + 32 = 64.8 + 32 = 96.8. Therefore, 36 degrees Celsius is equivalent to 96.8 degrees Fahrenheit.
| Celsius | Fahrenheit |
|---|---|
| 36 | 96.8 |

Applications of Temperature Conversion

The conversion of temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit has various applications in different fields. For example, in the field of medicine, body temperature is often measured in Celsius, but in some countries, it is still measured in Fahrenheit. Therefore, being able to convert between the two scales is essential for medical professionals. Similarly, in the field of engineering, temperature conversion is crucial for designing and operating systems that involve heat transfer, such as power plants, refrigeration systems, and air conditioning systems.
Real-World Examples
There are many real-world examples where temperature conversion is necessary. For instance, when traveling to a country that uses a different temperature scale, it’s essential to know how to convert temperatures to understand the weather forecast or to set the thermostat in a hotel room. Additionally, when cooking or baking, temperature conversion is crucial to ensure that the dish is prepared at the correct temperature.
For example, a recipe may call for an oven temperature of 180 degrees Celsius, but if the oven only has a Fahrenheit scale, the temperature needs to be converted to Fahrenheit before setting the oven. Using the conversion formula, we can calculate that 180 degrees Celsius is equivalent to 356 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Medical applications: body temperature measurement, pharmaceutical storage
- Engineering applications: heat transfer, power plants, refrigeration systems
- Culinary applications: cooking, baking, food storage
What is the freezing point of water in Celsius and Fahrenheit?
+The freezing point of water is 0 degrees Celsius and 32 degrees Fahrenheit.
What is the boiling point of water in Celsius and Fahrenheit?
+The boiling point of water is 100 degrees Celsius and 212 degrees Fahrenheit.
How do I convert 36 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit?
+To convert 36 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit, use the formula: Fahrenheit = (Celsius * 9/5) + 32. Plugging in the value of Celsius as 36, we get: Fahrenheit = (36 * 9/5) + 32 = 96.8.
In conclusion, converting 36 Celsius to Fahrenheit is a straightforward process that can be performed using a simple formula. Understanding the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales and their applications is essential in various fields, including medicine, engineering, and everyday life. By being able to convert temperatures between the two scales, we can ensure accurate communication and precise calculations, which are critical in many situations.