4 Advantages Of Biofuels
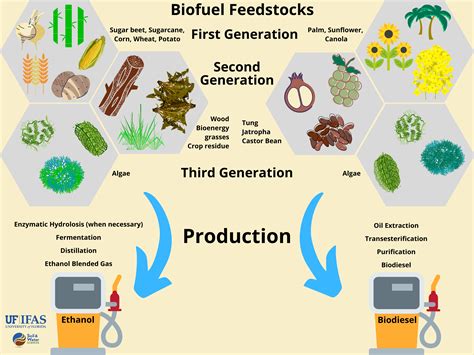
Biofuels, which are fuels produced from organic matter such as plants, algae, and agricultural and forestry waste, have gained significant attention in recent years due to their potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. The production and use of biofuels have several advantages, including reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, energy security, rural development, and improved air quality. In this article, we will discuss the advantages of biofuels and their potential to contribute to a more sustainable energy future.
Advantages of Biofuels

Biofuels have several advantages that make them an attractive alternative to fossil fuels. Some of the key advantages of biofuels include:
Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions
One of the most significant advantages of biofuels is their potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Biofuels are produced from organic matter, which absorbs carbon dioxide from the atmosphere as it grows. When biofuels are burned, they release the same amount of carbon dioxide that was absorbed during growth, resulting in a net reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the use of biofuels can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 80% compared to fossil fuels. For example, the production of biodiesel from soybeans or other oilseed crops can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 78% compared to traditional diesel fuel.
Energy Security
Another advantage of biofuels is their potential to improve energy security. Biofuels can be produced from a variety of feedstocks, including agricultural waste, forestry residues, and algae, which are available in many countries. This reduces dependence on imported fossil fuels and improves energy security. According to the United States Department of Energy, the use of biofuels can reduce dependence on foreign oil by up to 30%. For example, the production of ethanol from corn or sugarcane can reduce dependence on foreign oil and improve energy security.
Rural Development
Biofuels can also contribute to rural development by creating jobs and stimulating local economies. The production of biofuels requires a significant amount of labor, from planting and harvesting feedstocks to processing and transporting the final product. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations, the production of biofuels can create up to 10 jobs per million liters of biofuel produced. For example, the production of biodiesel from soybeans or other oilseed crops can create jobs in rural areas and stimulate local economies.
Improved Air Quality
Finally, biofuels can improve air quality by reducing emissions of air pollutants such as particulate matter, carbon monoxide, and hydrocarbons. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the use of biofuels can reduce emissions of air pollutants by up to 50% compared to fossil fuels. For example, the production of ethanol from corn or sugarcane can reduce emissions of air pollutants and improve air quality.
| Advantages of Biofuels | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions | Up to 80% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions |
| Energy Security | Up to 30% reduction in dependence on foreign oil |
| Rural Development | Up to 10 jobs per million liters of biofuel produced |
| Improved Air Quality | Up to 50% reduction in emissions of air pollutants |

In conclusion, the advantages of biofuels make them an attractive alternative to fossil fuels. The reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, energy security, rural development, and improved air quality are just a few of the benefits of biofuels. As the world continues to transition to a more sustainable energy future, it is likely that biofuels will play an increasingly important role.
What are the main advantages of biofuels?
+The main advantages of biofuels are reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, energy security, rural development, and improved air quality. Biofuels can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 80%, improve energy security by reducing dependence on foreign oil, create jobs and stimulate local economies, and improve air quality by reducing emissions of air pollutants.
What are the different types of biofuels?
+There are several types of biofuels, including ethanol, biodiesel, and biogas. Ethanol is produced from fermented plant materials such as corn or sugarcane, biodiesel is produced from vegetable oils or animal fats, and biogas is produced from the anaerobic digestion of organic matter.
What is the future of biofuels?
+The future of biofuels is promising, with many countries investing in the production and use of biofuels. The International Energy Agency (IEA) predicts that biofuels will play an increasingly important role in the global energy mix, with the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve energy security. However, there are also challenges to be addressed, such as the need for sustainable feedstocks and the development of more efficient production technologies.