9.62 Standard Deviation

The standard deviation is a statistical measure that represents the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. A standard deviation of 9.62 indicates that the data points in the set are spread out over a range of values, with some points being significantly higher or lower than the mean. In this case, the standard deviation is relatively large, suggesting that the data is highly variable.
Understanding Standard Deviation
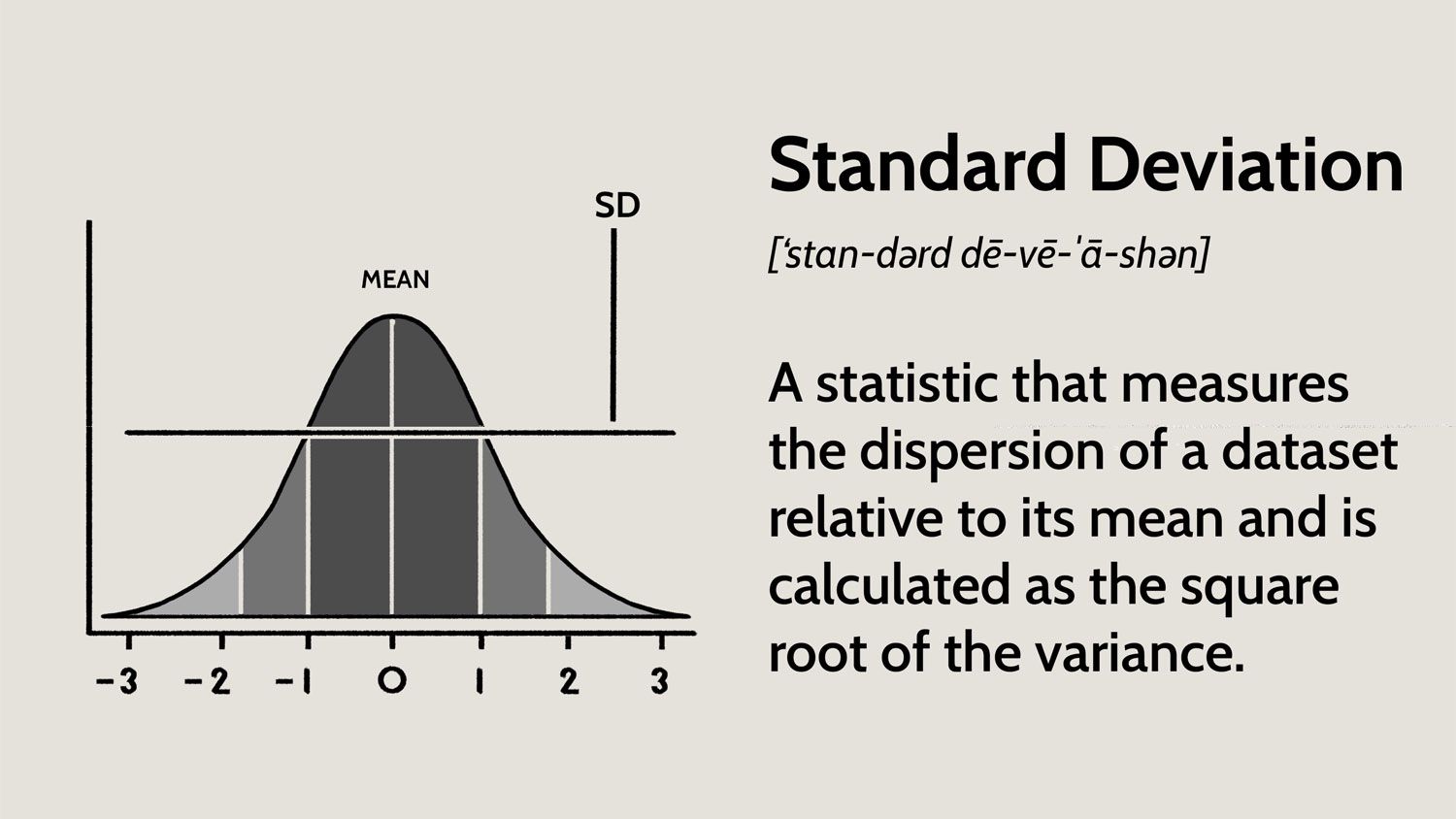
Standard deviation is calculated as the square root of the variance, which is the average of the squared differences from the mean. The formula for standard deviation is: σ = √[(Σ(x - μ)^2) / (n - 1)], where σ is the standard deviation, x is each individual data point, μ is the mean, and n is the number of data points. A standard deviation of 9.62 would indicate that approximately 68% of the data points fall within one standard deviation of the mean, or between the mean - 9.62 and the mean + 9.62.
Interpreting Standard Deviation
A standard deviation of 9.62 can be interpreted in different ways depending on the context of the data. For example, if the data represents stock prices, a standard deviation of 9.62 might indicate that the stock is highly volatile, with large fluctuations in price over time. On the other hand, if the data represents the heights of individuals, a standard deviation of 9.62 might indicate that there is significant variation in height within the population. It’s essential to consider the mean and the context of the data when interpreting the standard deviation.
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Standard Deviation | 9.62 |
| Variance | 92.5424 |
| Mean | varies |

Applications of Standard Deviation

Standard deviation has numerous applications in various fields, including finance, engineering, and social sciences. In finance, standard deviation is used to measure the risk of an investment, with higher standard deviations indicating greater risk. In engineering, standard deviation is used to measure the variability of a process, with lower standard deviations indicating greater precision. In social sciences, standard deviation is used to measure the variability of a population, with higher standard deviations indicating greater diversity.
Calculating Standard Deviation
Calculating standard deviation involves several steps, including calculating the mean, calculating the deviations from the mean, squaring the deviations, and averaging the squared deviations. The following is an example of how to calculate standard deviation: suppose we have a dataset of exam scores with values 70, 80, 90, 75, and 85. First, we calculate the mean: (70 + 80 + 90 + 75 + 85) / 5 = 80. Then, we calculate the deviations from the mean: (70 - 80), (80 - 80), (90 - 80), (75 - 80), and (85 - 80). Next, we square the deviations: (-10)^2, 0^2, 10^2, (-5)^2, and 5^2. Finally, we average the squared deviations and take the square root to get the standard deviation.
- Mean: 80
- Deviations: -10, 0, 10, -5, 5
- Squared Deviations: 100, 0, 100, 25, 25
- Average Squared Deviation: (100 + 0 + 100 + 25 + 25) / 5 = 50
- Standard Deviation: √50 ≈ 7.07
What does a standard deviation of 9.62 indicate?
+A standard deviation of 9.62 indicates that the data points in the set are spread out over a range of values, with some points being significantly higher or lower than the mean. This suggests that the data is highly variable.
How is standard deviation calculated?
+Standard deviation is calculated as the square root of the variance, which is the average of the squared differences from the mean. The formula for standard deviation is: σ = √[(Σ(x - μ)^2) / (n - 1)], where σ is the standard deviation, x is each individual data point, μ is the mean, and n is the number of data points.
In conclusion, a standard deviation of 9.62 is a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. It is essential to consider the context of the data and the mean when interpreting the standard deviation. Standard deviation has numerous applications in various fields, including finance, engineering, and social sciences. By understanding how to calculate and interpret standard deviation, we can gain valuable insights into the characteristics of a dataset.