Big Black Flying Bug

The big black flying bug is a common description for various insects that match this general appearance. However, to narrow down the identification, it's crucial to consider additional characteristics such as size, shape, wings, and behavior. One of the most recognizable big black flying bugs is the cockchafer beetle, also known as the May bug or June bug. These beetles are known for their large size, typically ranging from 1.5 to 2.5 cm in length, and their shiny black elytra (wing covers). They are nocturnal, flying towards light sources at night, which often brings them into human notice.
Types of Big Black Flying Bugs

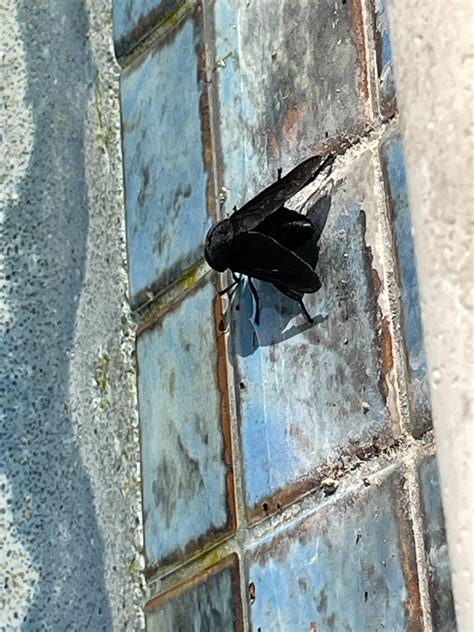
Several species of insects can be classified as big black flying bugs, including beetles, flies, and wasps. Beetles are one of the most diverse groups of insects, with over 400,000 known species, many of which are black and capable of flight. The black fly, known for its painful bite, is another example. These small to medium-sized flies are often found near water sources, as their larvae are aquatic. Wasps, such as the paper wasp and certain species of hornets, can also appear as big black flying bugs, although many have yellow or white markings.
Characteristics for Identification
To accurately identify a big black flying bug, observing its body shape, wing structure, and behavior is essential. For instance, beetles have a hard exoskeleton and typically fold their wings under their elytra when not flying. Flies have only one pair of wings, with the hindwings being reduced to small halteres that help with balance during flight. Wasps and hornets are generally more slender and have a narrow waist between their abdomen and thorax. Understanding these characteristics can help in distinguishing between different types of big black flying bugs.
| Insect Type | Description | Size |
|---|---|---|
| Cockchafer Beetle | Shiny black elytra, nocturnal | 1.5-2.5 cm |
| Black Fly | Small to medium, aquatic larvae | 1-5 mm |
| Paper Wasp | Slender, narrow waist, builds paper nests | 1.5-2 cm |
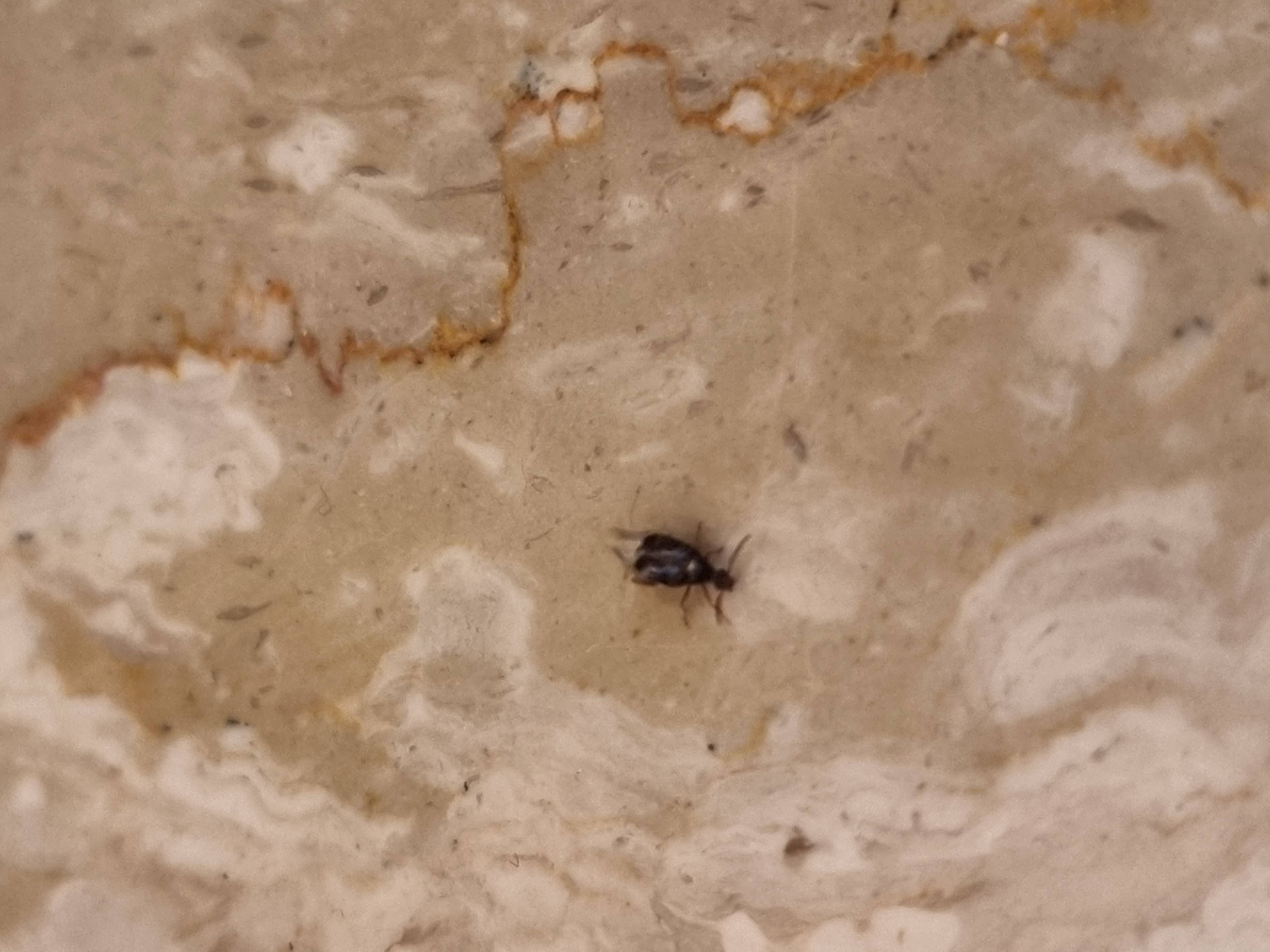

Behavior and Habitat
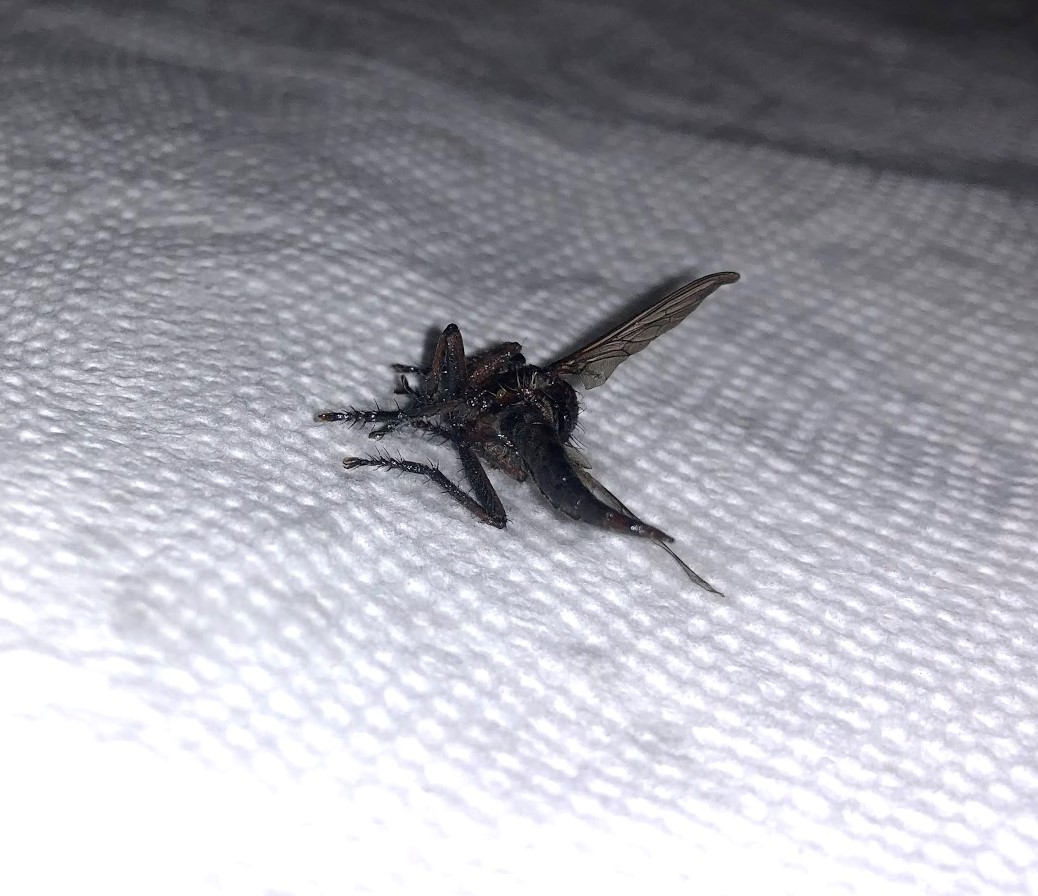

The behavior and habitat of big black flying bugs can vary significantly depending on the species. Nocturnal species, like many beetles, are active at night and often attracted to artificial light sources, which can lead them into homes or buildings. Diurnal species, such as certain wasps and flies, are active during the day and may be found near food sources, such as sweet substances, proteins, or pollens. Understanding the life cycle of these insects, including their larval stages and feeding habits, can also provide insights into their identification and control.
Control and Management
For individuals concerned about big black flying bugs, whether due to nuisance, fear of bites or stings, or potential for property damage, several control measures can be considered. Sealing entry points to prevent bugs from entering homes or buildings is a first step. Eliminating standing water can help reduce the presence of aquatic larvae of flies and mosquitoes. Using traps, such as UV light traps for nocturnal beetles or sticky traps for flies, can also be effective. In cases where an infestation poses a significant problem, consulting a pest control professional may be necessary.
How can I prevent big black flying bugs from entering my home?
+To prevent big black flying bugs from entering your home, ensure that all windows and doors are properly sealed. Installing screens on windows and vents can also help keep bugs out. Additionally, reducing outdoor lighting at night or using yellow bulbs, which are less attractive to nocturnal insects, can decrease the number of bugs around your home.
Are all big black flying bugs harmful?
+No, not all big black flying bugs are harmful. While some, like black flies and certain wasps, can bite or sting, others are harmless to humans. Beetles, for example, do not bite or sting and are primarily nuisance pests. Understanding the specific type of bug and its behavior can help determine the level of concern.
In conclusion, the term “big black flying bug” encompasses a wide range of insect species, each with unique characteristics, behaviors, and habitats. By understanding these specifics, individuals can better identify the bugs they encounter and take appropriate measures to manage their presence, whether it be for comfort, safety, or environmental reasons.