Broccoli Nutrition Facts: Unlock Health Benefits

Broccoli, a cruciferous vegetable, has been a staple in many cuisines around the world for its nutritional value and potential health benefits. It is a rich source of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that can help protect against various diseases. With its high nutritional content, broccoli has become a popular ingredient in healthy diets, and its benefits are backed by scientific research. In this article, we will delve into the nutritional facts of broccoli and explore its potential health benefits.
Nutritional Profile of Broccoli
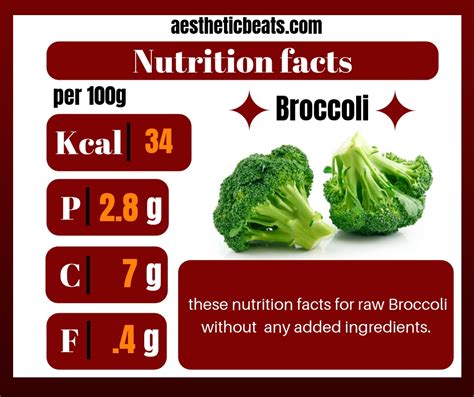
Broccoli is an excellent source of vitamins C and K, folate, and fiber. It also contains a range of other essential nutrients, including vitamin A, vitamin B6, and potassium. One cup of chopped broccoli (approximately 55 grams) contains only 55 calories, making it a low-calorie and nutrient-dense food. The nutritional profile of broccoli is summarized in the following table:
| Nutrient | Amount per 1 cup (55g) |
|---|---|
| Calories | 55 |
| Vitamin C | 101mg (168% DV) |
| Vitamin K | 116mcg (145% DV) |
| Folate | 106mcg (26% DV) |
| Fiber | 2.6g (10% DV) |
| Vitamin A | 120mcg (13% DV) |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.2mg (10% DV) |
| Potassium | 450mg (13% DV) |

Health Benefits of Broccoli
The high nutritional content of broccoli makes it a potential candidate for reducing the risk of various diseases. Some of the key health benefits of broccoli include:
- Cancer prevention: The sulforaphane present in broccoli has been shown to have anti-cancer properties, particularly in reducing the risk of colon, breast, and prostate cancers.
- Cardiovascular health: The fiber, potassium, and vitamin C in broccoli can help lower cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and inflammation, all of which are risk factors for heart disease.
- Immune system support: The vitamin C in broccoli can help boost the immune system, reducing the severity of colds and flu.
- Digestive health: The fiber in broccoli can help regulate bowel movements, prevent constipation, and support the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
In addition to these benefits, broccoli also contains a range of phytochemicals, including isothiocyanates and indoles, which have been shown to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. The glucosinolates present in broccoli have also been found to have anti-cancer properties.
Cooking and Preparation Methods

The way broccoli is cooked and prepared can affect its nutritional content. Steaming is a good method for preserving the vitamins and minerals in broccoli, as it helps retain the water-soluble vitamins. Roasting can also be a healthy option, as it brings out the natural sweetness in broccoli and can help retain the fiber and antioxidants. However, overcooking broccoli can lead to a loss of nutrients, particularly vitamin C and B vitamins.
Nutrient Retention during Cooking
The following table shows the retention of nutrients in broccoli after different cooking methods:
| Cooking Method | Vitamin C Retention | Fiber Retention |
|---|---|---|
| Steaming | 80-90% | 90-95% |
| Roasting | 70-80% | 85-90% |
| Boiling | 50-60% | 70-80% |
| Microwaving | 60-70% | 80-85% |
It is essential to note that the nutrient retention can vary depending on the cooking time, temperature, and method. To maximize the nutritional benefits of broccoli, it is recommended to cook it for a short period, using minimal water, and at a low temperature.
What are the potential side effects of consuming broccoli?
+Broccoli is generally considered safe to eat, but some people may experience gas, bloating, or digestive discomfort due to its high fiber and raffinose content. Additionally, individuals with thyroid problems should consult their doctor before consuming large amounts of broccoli, as it may interfere with thyroid function.
Can broccoli be grown at home?
+Yes, broccoli can be grown at home, either in a garden or in containers. It prefers well-draining soil, full sun, and cooler temperatures. Broccoli is a cool-season crop and can be planted in early spring or late summer/early fall.
In conclusion, broccoli is a nutrient-dense food that offers a range of health benefits, from cancer prevention to digestive health support. By incorporating broccoli into a healthy diet and cooking it using methods that preserve its nutrients, individuals can maximize its potential benefits. With its rich nutritional profile and potential health benefits, broccoli is an excellent addition to a balanced diet.