Capping Rmove Polluantat

Capping and removing pollutants from contaminated sites is a critical process in environmental remediation. The goal of this process is to prevent further contamination of the environment and to restore the site to a safe and healthy condition. There are several techniques used to cap and remove pollutants, including excavation, pump and treat, and bioremediation. Each of these techniques has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of technique depends on the type and extent of the contamination, as well as the geology and hydrology of the site.
Techniques for Capping and Removing Pollutants
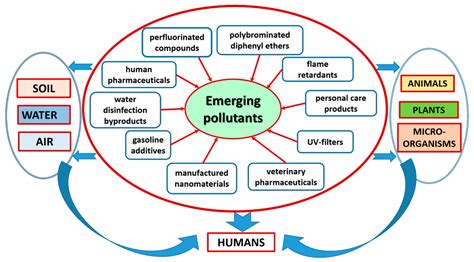
One of the most common techniques used to cap and remove pollutants is excavation. This involves digging up the contaminated soil and removing it to a landfill or treatment facility. Excavation is often used for sites with high levels of contamination, such as those with volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). However, excavation can be expensive and disruptive, and it may not be effective for sites with deep or widespread contamination.
Pump and Treat Method
The pump and treat method involves extracting contaminated groundwater from the site and treating it to remove pollutants. This technique is often used in combination with excavation, and it can be effective for sites with chlorinated solvents or petroleum hydrocarbons. The pump and treat method typically involves installing a network of wells and pumps to extract the contaminated groundwater, which is then treated using techniques such as air stripping or activated carbon adsorption.
| Technique | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Excavation | Digging up contaminated soil and removing it to a landfill or treatment facility | Effective for high levels of contamination, can be used for a variety of pollutants | Expensive, disruptive, may not be effective for deep or widespread contamination |
| Pump and Treat | Extracting contaminated groundwater and treating it to remove pollutants | Effective for chlorinated solvents and petroleum hydrocarbons, can be used in combination with excavation | May not be effective for deep or widespread contamination, can be expensive |
| Bioremediation | Using microorganisms to break down pollutants | Effective for a variety of pollutants, can be less expensive than excavation or pump and treat | May not be effective for high levels of contamination, can be slow |

Bioremediation Technique
Bioremediation is a technique that uses microorganisms to break down pollutants. This technique is often used for sites with petroleum hydrocarbons or polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Bioremediation can be less expensive than excavation or pump and treat, and it can be effective for a variety of pollutants. However, bioremediation may not be effective for high levels of contamination, and it can be slow.
Factors Affecting Bioremediation
There are several factors that can affect the effectiveness of bioremediation, including temperature, pH, and oxygen levels. Microorganisms typically thrive in temperatures between 15°C and 30°C, and pH levels between 6.5 and 8.5. Oxygen levels can also impact bioremediation, as microorganisms require oxygen to break down pollutants.
In addition to these factors, the type and concentration of pollutants can also impact bioremediation. Some pollutants, such as chlorinated solvents, may be more resistant to biodegradation than others. The presence of other contaminants, such as heavy metals, can also impact bioremediation.
What is the most effective technique for removing pollutants from contaminated sites?
+The most effective technique for removing pollutants from contaminated sites depends on the type and extent of the contamination, as well as the geology and hydrology of the site. Excavation, pump and treat, and bioremediation are all effective techniques, but the choice of technique depends on the specific site conditions.
How long does bioremediation take to remove pollutants from a contaminated site?
+The length of time it takes for bioremediation to remove pollutants from a contaminated site depends on several factors, including the type and concentration of pollutants, the presence of other contaminants, and the site conditions. Bioremediation can take several months to several years to complete, and it requires regular monitoring and maintenance to ensure its effectiveness.
In conclusion, capping and removing pollutants from contaminated sites is a critical process in environmental remediation. The choice of technique depends on the type and extent of the contamination, as well as the geology and hydrology of the site. Excavation, pump and treat, and bioremediation are all effective techniques, but they require careful planning and execution to ensure their effectiveness. By understanding the factors that impact these techniques and developing a comprehensive remediation plan, it’s possible to restore contaminated sites to a safe and healthy condition.
