Causal Inference Mastery: Distributionfree Guide

Causal inference is a crucial aspect of statistical analysis, as it enables researchers to understand the relationships between variables and make informed decisions. Traditional methods of causal inference often rely on distributional assumptions, which can be restrictive and limiting. However, with the advent of distribution-free methods, researchers can now estimate causal effects without being bound by these assumptions. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of causal inference, exploring its fundamental concepts, distribution-free methods, and applications.
Introduction to Causal Inference

Causal inference is concerned with understanding the causal relationships between variables. It involves estimating the effect of a treatment or intervention on an outcome variable, while accounting for potential confounding factors. The goal of causal inference is to provide a clear understanding of the causal mechanisms underlying a phenomenon, which is essential for making informed decisions in various fields, such as medicine, economics, and social sciences.
The traditional approach to causal inference relies on parametric models, which assume a specific distribution for the data. However, these assumptions can be restrictive, and violations of these assumptions can lead to biased estimates. Distribution-free methods, on the other hand, do not rely on parametric assumptions, making them more flexible and robust.
Causal graphs are a fundamental tool in causal inference, as they provide a visual representation of the causal relationships between variables. These graphs consist of nodes, which represent variables, and edges, which represent the causal relationships between them. Causal Bayesian networks are a type of causal graph that can be used to model complex causal relationships.
Distribution-Free Methods for Causal Inference
Several distribution-free methods have been developed for causal inference, including instrumental variable analysis, regression discontinuity design, and matching methods. These methods do not rely on parametric assumptions, making them more robust to model misspecification.
Instrumental variable analysis is a popular method for estimating causal effects in the presence of confounding variables. This method relies on an instrumental variable, which is a variable that affects the treatment but not the outcome directly. Instrumental variable estimation can be used to estimate the causal effect of the treatment on the outcome.
Regression discontinuity design is another distribution-free method that can be used to estimate causal effects. This method relies on a discontinuity in the treatment assignment, which can be used to identify the causal effect of the treatment.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Instrumental Variable Analysis | Estimates causal effects using an instrumental variable |
| Regression Discontinuity Design | Estimates causal effects using a discontinuity in treatment assignment |
| Matching Methods | Estimates causal effects by matching treated and control units |
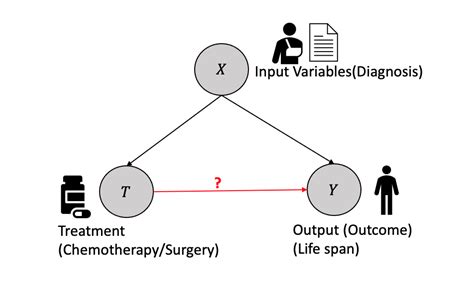
Applications of Causal Inference

Causal inference has a wide range of applications in various fields, including medicine, economics, and social sciences. In medicine, causal inference can be used to estimate the effect of a treatment on a disease outcome. In economics, causal inference can be used to estimate the effect of a policy intervention on economic outcomes.
Randomized controlled trials are a popular method for estimating causal effects in medicine. These trials involve randomly assigning participants to a treatment or control group, which can provide an unbiased estimate of the causal effect. However, confounding variables can still affect the estimate, and distribution-free methods can be used to address these confounding variables.
In economics, quasi-experiments are often used to estimate causal effects. These experiments involve exploiting natural experiments or discontinuities in treatment assignment to estimate the causal effect. Instrumental variable estimation can be used to estimate the causal effect of a policy intervention on economic outcomes.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the advances in causal inference, there are still several challenges that need to be addressed. One of the major challenges is the presence of unmeasured confounding variables, which can affect the estimate of the causal effect. Distribution-free methods can be used to address these confounding variables, but they often require careful consideration of the underlying assumptions.
Another challenge is the interpretation of causal estimates. Causal estimates can be difficult to interpret, especially in the presence of multiple causal pathways. Causal mediation analysis can be used to estimate the causal effect of a treatment on an outcome through a mediator variable.
Machine learning methods are being increasingly used in causal inference, especially for estimating causal effects in complex data settings. These methods can provide more robust estimates of causal effects, but they often require careful consideration of the underlying assumptions and may not always provide unbiased estimates.
What is the difference between causal inference and statistical inference?
+Causal inference is concerned with understanding the causal relationships between variables, while statistical inference is concerned with understanding the statistical relationships between variables. Causal inference requires a deeper understanding of the underlying causal mechanisms, while statistical inference can be used to estimate statistical relationships without considering the underlying causal mechanisms.
What are the advantages of distribution-free methods for causal inference?
+Distribution-free methods can provide more robust estimates of causal effects, especially in the presence of model misspecification. These methods do not rely on parametric assumptions, making them more flexible and robust. However, these methods often require careful consideration of the underlying assumptions and may not always provide unbiased estimates.
What are the challenges of interpreting causal estimates?
+Causal estimates can be difficult to interpret, especially in the presence of multiple causal pathways. Causal mediation analysis can be used to estimate the causal effect of a treatment on an outcome through a mediator variable. However, interpreting causal estimates requires a deep understanding of the underlying causal mechanisms and the potential biases that can affect the estimate.
