Cell Cell Communication: Boosts Health

Cell-to-cell communication is a vital process that occurs within the human body, allowing cells to exchange information and coordinate their actions to maintain overall health. This complex process involves the exchange of signals between cells, which can be achieved through various mechanisms, including direct cell-to-cell contact, signaling molecules, and electrical impulses. In this article, we will delve into the world of cell-to-cell communication, exploring its importance, mechanisms, and impact on human health.
Introduction to Cell-to-Cell Communication
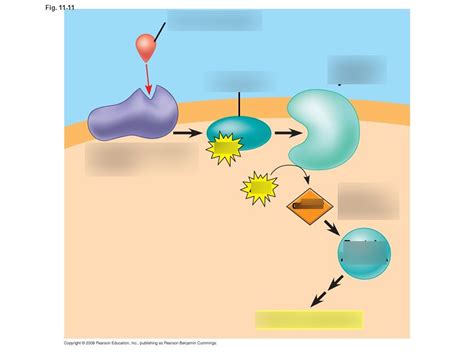
Cell-to-cell communication is a fundamental aspect of cellular biology, enabling cells to respond to their environment, adapt to changes, and work together to maintain tissue and organ function. This process is essential for various physiological processes, including development, growth, and repair. Cells use a range of signaling molecules, such as hormones, neurotransmitters, and growth factors, to communicate with each other. These signaling molecules can bind to specific receptors on the surface of target cells, triggering a response that can lead to changes in gene expression, cell behavior, and overall physiology.
Types of Cell-to-Cell Communication
There are several types of cell-to-cell communication, including autocrine, paracrine, endocrine, and synaptic signaling. Autocrine signaling occurs when a cell produces signaling molecules that bind to receptors on the same cell, leading to changes in cell behavior. Paracrine signaling involves the release of signaling molecules by one cell that bind to receptors on nearby cells, influencing their behavior. Endocrine signaling occurs when signaling molecules are released into the bloodstream, allowing them to reach distant cells and influence their behavior. Synaptic signaling, on the other hand, involves the transmission of electrical and chemical signals between neurons, enabling communication within the nervous system.
| Type of Signaling | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Autocrine Signaling | Signaling molecules bind to receptors on the same cell | Cell growth and proliferation |
| Paracrine Signaling | Signaling molecules bind to receptors on nearby cells | Wound healing and tissue repair |
| Endocrine Signaling | Signaling molecules are released into the bloodstream | Hormone regulation and metabolic control |
| Synaptic Signaling | Transmission of electrical and chemical signals between neurons | Nervous system function and behavior |
Importance of Cell-to-Cell Communication in Health and Disease
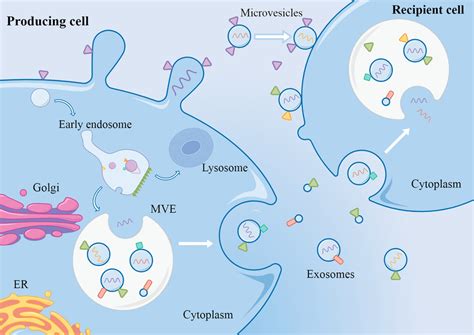
Cell-to-cell communication is essential for maintaining health and preventing disease. Disruptions in cell-to-cell communication can lead to a range of diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, and metabolic disorders. For example, cancer cells often exhibit altered cell-to-cell communication, leading to uncontrolled growth and invasion of surrounding tissues. In contrast, healthy cell-to-cell communication is essential for maintaining tissue homeostasis, regulating the immune response, and promoting wound healing.
Role of Cell-to-Cell Communication in Cancer
Cancer cells often exhibit disrupted cell-to-cell communication, leading to the loss of normal cellular behavior and the acquisition of malignant characteristics. This can involve the production of abnormal signaling molecules, the expression of aberrant receptors, or the disruption of normal signaling pathways. For example, cancer cells may produce high levels of growth factors, leading to excessive cell proliferation and tumor growth. Conversely, the restoration of normal cell-to-cell communication can inhibit cancer cell growth and promote apoptosis (cell death).
- Disrupted cell-to-cell communication in cancer can lead to the loss of normal cellular behavior
- Abnormal signaling molecules and receptors can contribute to cancer development and progression
- Restoration of normal cell-to-cell communication can inhibit cancer cell growth and promote apoptosis
Future Directions and Implications
The study of cell-to-cell communication has significant implications for our understanding of human health and disease. Further research into the mechanisms and regulation of cell-to-cell communication can provide valuable insights into the development of novel therapeutic strategies. For example, the identification of key signaling molecules and pathways can lead to the development of targeted therapies, while the understanding of cell-to-cell communication in the context of cancer can inform the development of immunotherapies.
Emerging Technologies and Therapies
Emerging technologies, such as gene editing and gene therapy, hold great promise for the treatment of diseases related to disrupted cell-to-cell communication. For example, gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR/Cas9, can be used to correct genetic mutations that disrupt cell-to-cell communication, while gene therapy can be used to introduce healthy copies of genes involved in cell-to-cell communication. Additionally, the development of novel biomaterials and bioengineered systems can provide new opportunities for the study and manipulation of cell-to-cell communication.
- Gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR/Cas9, can be used to correct genetic mutations that disrupt cell-to-cell communication
- Gene therapy can be used to introduce healthy copies of genes involved in cell-to-cell communication
- Novel biomaterials and bioengineered systems can provide new opportunities for the study and manipulation of cell-to-cell communication
What is the importance of cell-to-cell communication in human health?
+Cell-to-cell communication is essential for maintaining health and preventing disease. It allows cells to exchange information and coordinate their actions to maintain tissue and organ function, and disruptions in cell-to-cell communication can lead to a range of diseases.
How does cell-to-cell communication contribute to cancer development and progression?
+Disrupted cell-to-cell communication can contribute to cancer development and progression by leading to the loss of normal cellular behavior, the production of abnormal signaling molecules, and the expression of aberrant receptors. This can result in uncontrolled cell growth, invasion of surrounding tissues, and the acquisition of malignant characteristics.
What are the potential therapeutic strategies for diseases related to disrupted cell-to-cell communication?
+Potential therapeutic strategies for diseases related to disrupted cell-to-cell communication include targeted therapies, immunotherapies, gene editing, and gene therapy. These approaches can be used to restore normal cell-to-cell communication, inhibit disease progression, and promote tissue repair and regeneration.
