Cervical Polyps Guide: Symptoms Explained

Cervical polyps are growths that occur on the cervix, which is the lower part of the uterus in the female reproductive system. These growths are usually benign, meaning they are non-cancerous, and are relatively common, affecting up to 10% of women at some point in their lives. Understanding the symptoms of cervical polyps is crucial for early detection and treatment, which can help prevent potential complications and ensure the best possible outcomes for reproductive health.
The symptoms of cervical polyps can vary from woman to woman, but there are several common signs that may indicate their presence. One of the most frequent symptoms is abnormal vaginal bleeding, which can include bleeding after sexual intercourse, bleeding between menstrual periods, or prolonged menstrual periods. Women may also experience an increase in vaginal discharge, which can be clear, cloudy, or even bloody. In some cases, cervical polyps may cause no symptoms at all, and their presence may only be discovered during a routine pelvic examination or Pap test.
Causes and Risk Factors
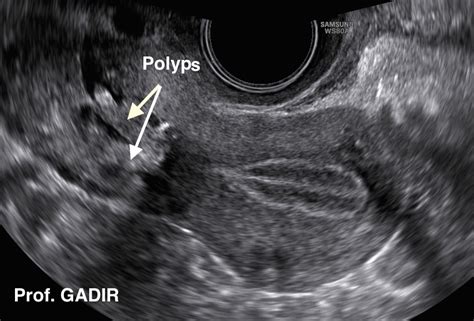
Cervical polyps are thought to be caused by an overgrowth of cells on the cervix, which can be triggered by a variety of factors, including hormonal changes, inflammation, and infection. Women who are overweight or obese may be at higher risk of developing cervical polyps, as excess weight can lead to hormonal imbalances and increased inflammation in the body. Additionally, women who have a history of cervical polyps are more likely to develop new polyps in the future.
Other risk factors for cervical polyps include hormonal birth control, which can affect the balance of hormones in the body and increase the risk of polyp growth. Women who are over 40 years old may also be at higher risk, as the risk of cervical polyps tends to increase with age. Understanding these risk factors can help women take preventive measures and be more aware of the potential symptoms of cervical polyps.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Cervical polyps are typically diagnosed through a pelvic examination and Pap test, which can help identify abnormal cell growth on the cervix. In some cases, a colposcopy may be performed, which uses a special microscope to examine the cervix and vagina for abnormal cell growth. If a cervical polyp is suspected, a biopsy may be taken to confirm the diagnosis and rule out any potential cancer.
Treatment for cervical polyps usually involves removal of the polyp, which can be done in a doctor's office or clinic. The procedure is typically quick and relatively painless, and can help alleviate symptoms and prevent potential complications. In some cases, women may be prescribed hormonal medications to help regulate hormonal imbalances and prevent the growth of new polyps.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Abnormal vaginal bleeding | Bleeding after sex, between periods, or prolonged periods |
| Increased vaginal discharge | Clear, cloudy, or bloody discharge |
| No symptoms | Polyps may be asymptomatic and only discovered during a routine exam |

Complications and Prevention
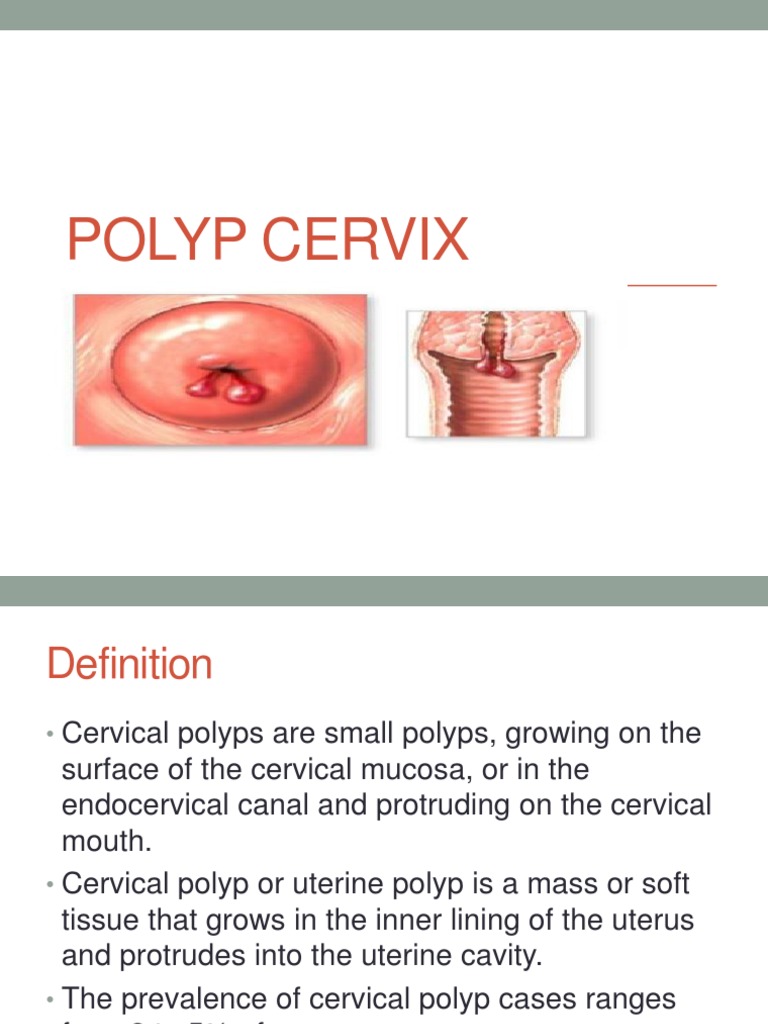
If left untreated, cervical polyps can lead to several potential complications, including infertility and miscarriage. Women who have untreated cervical polyps may also be at higher risk of developing cervical cancer, which can be life-threatening if not caught early. To prevent these complications, women can take several steps, including practicing safe sex to reduce the risk of infection, maintaining a healthy weight to reduce hormonal imbalances, and attending regular pelvic examinations to ensure early detection and treatment of cervical polyps.
Additionally, women can reduce their risk of developing cervical polyps by quitting smoking, which can help reduce inflammation and improve overall reproductive health. Women who are sexually active should also consider getting regular HPV vaccinations to protect against the human papillomavirus, which can increase the risk of cervical cancer.
Natural Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
While there are no guaranteed natural remedies for cervical polyps, women can make several lifestyle changes to help reduce their risk and alleviate symptoms. These include eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, staying hydrated to help flush out toxins, and practicing stress-reducing techniques such as yoga or meditation to help manage hormonal imbalances.
Women can also consider taking supplements such as omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D, which can help reduce inflammation and promote overall reproductive health. However, it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements or making significant lifestyle changes.
What are the symptoms of cervical polyps?
+The symptoms of cervical polyps can include abnormal vaginal bleeding, increased vaginal discharge, and no symptoms at all. Women may experience bleeding after sex, between periods, or prolonged periods, and may also notice an increase in clear, cloudy, or bloody discharge.
How are cervical polyps diagnosed?
+Cervical polyps are typically diagnosed through a pelvic examination and Pap test, which can help identify abnormal cell growth on the cervix. A colposcopy may also be performed to examine the cervix and vagina for abnormal cell growth, and a biopsy may be taken to confirm the diagnosis and rule out any potential cancer.
Can cervical polyps be prevented?
+While there is no guaranteed way to prevent cervical polyps, women can reduce their risk by practicing safe sex, maintaining a healthy weight, and attending regular pelvic examinations. Women can also reduce their risk by quitting smoking, getting regular HPV vaccinations, and eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
