Crayfish Food Chain: Understanding Producers
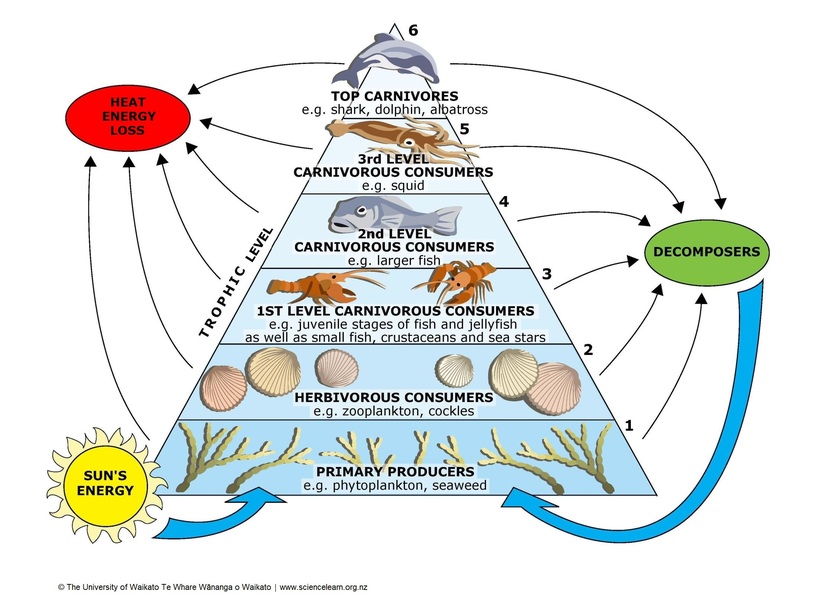
The crayfish food chain is a complex network of relationships between various species in an ecosystem, with crayfish playing a crucial role as both predators and prey. At the base of this food chain are the producers, which are organisms that produce their own food through photosynthesis. In the context of a crayfish's ecosystem, producers are primarily composed of aquatic plants and algae. These organisms form the foundation of the food chain, providing energy and nutrients for the entire ecosystem.
Producers in a crayfish's ecosystem can be found in various forms, including phytoplankton, which are microscopic plant-like organisms that drift in the water column, and macrophytes, which are larger aquatic plants such as water lilies and cattails. These producers are essential for the survival of crayfish, as they provide food and shelter for them. For example, crayfish feed on detritus, which is the decomposing matter of dead plants and animals, as well as on algae that grows on rocks and other submerged surfaces.
Primary Producers in Crayfish Ecosystems

Primary producers in crayfish ecosystems are the foundation of the food chain, and they can be categorized into several groups. These include green algae, diatoms, and cyanobacteria, which are all types of phytoplankton. These microorganisms are capable of photosynthesis, producing organic compounds that serve as a source of energy for other organisms in the ecosystem. In addition to phytoplankton, macroalgae such as seaweeds and aquatic vascular plants like water lilies and cattails also play important roles as primary producers.
The productivity of primary producers in crayfish ecosystems can be influenced by various factors, including light intensity, water temperature, and nutrient availability. For example, an increase in light intensity can stimulate the growth of phytoplankton, leading to an increase in the overall productivity of the ecosystem. Similarly, changes in water temperature can affect the growth and distribution of aquatic plants, which can have cascading effects on the entire food chain.
Types of Producers in Crayfish Ecosystems
There are several types of producers that can be found in crayfish ecosystems, each with its own unique characteristics and roles. These include:
- Phytoplankton: Microscopic plant-like organisms that drift in the water column, such as green algae and diatoms.
- Macrophytes: Larger aquatic plants such as water lilies and cattails, which provide food and shelter for crayfish.
- Periphyton: A complex community of algae, bacteria, and other microorganisms that grow on submerged surfaces, such as rocks and aquatic plants.
- Detritus: The decomposing matter of dead plants and animals, which serves as a source of energy for crayfish and other organisms.
| Producer Type | Description | Role in Ecosystem |
|---|---|---|
| Phytoplankton | Microscopic plant-like organisms | Primary production, food source for zooplankton |
| Macrophytes | Larger aquatic plants | Food and shelter for crayfish, habitat for other organisms |
| Periphyton | Complex community of algae and microorganisms | Primary production, food source for grazers |
| Detritus | Decomposing matter of dead plants and animals | Energy source for crayfish and other organisms |

In conclusion, producers play a vital role in crayfish ecosystems, providing the energy and nutrients necessary to support the entire food chain. Understanding the different types of producers and their roles in the ecosystem is essential for managing and conserving crayfish populations, as well as maintaining the overall health and balance of the ecosystem.
What is the primary source of energy for crayfish in an ecosystem?
+The primary source of energy for crayfish in an ecosystem is the producers, which include aquatic plants and algae. These organisms produce their own food through photosynthesis, providing energy and nutrients for the entire ecosystem.
How do changes in water temperature affect the productivity of primary producers in crayfish ecosystems?
+Changes in water temperature can affect the growth and distribution of aquatic plants, which can have cascading effects on the entire food chain. For example, an increase in water temperature can stimulate the growth of phytoplankton, leading to an increase in the overall productivity of the ecosystem.
What is the role of detritus in crayfish ecosystems?
+Detritus serves as a source of energy for crayfish and other organisms in the ecosystem. It is the decomposing matter of dead plants and animals, and provides nutrients and energy for the entire food chain.