E C G Leads Position

The electrocardiogram (ECG) is a fundamental tool in cardiology, used to record the electrical activity of the heart. To obtain an accurate ECG reading, it is crucial to position the leads correctly on the body. The standard 12-lead ECG involves placing 10 electrodes on the chest and limbs, which requires a thorough understanding of the lead positions and their corresponding views of the heart.
Introduction to ECG Leads Positioning
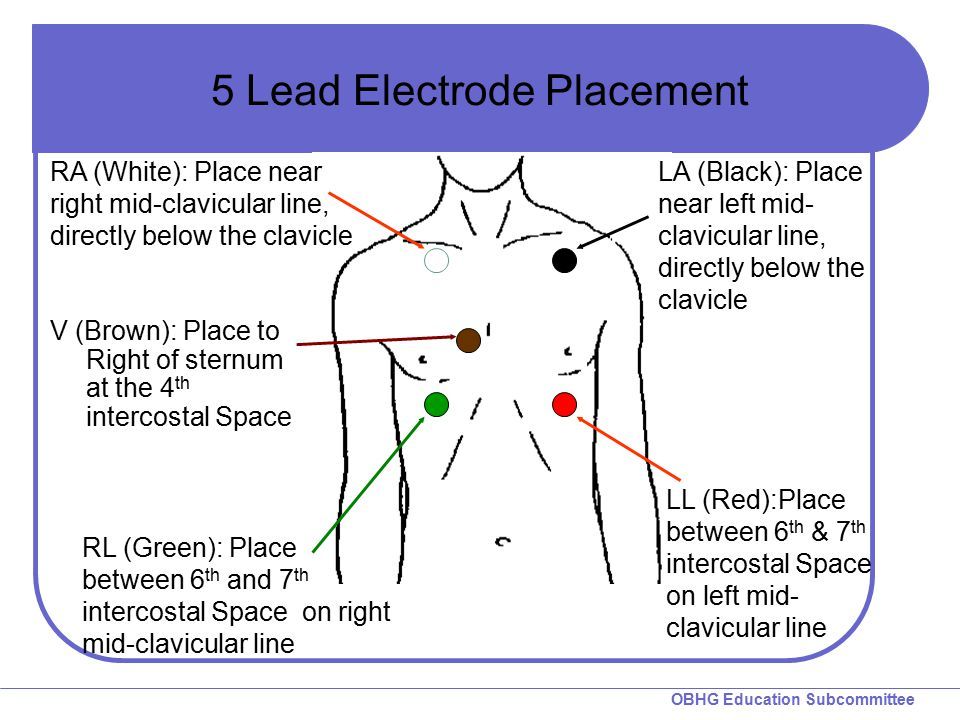
ECG leads are the pathways through which the electrical activity of the heart is recorded. The 12-lead ECG consists of 12 different views of the heart, each providing unique information about the heart’s electrical activity. The leads are divided into two main categories: the limb leads and the chest leads. The limb leads (I, II, III, aVR, aVL, and aVF) record the electrical activity of the heart from the limbs, while the chest leads (V1-V6) record the activity from the chest.
Limb Leads Positioning
The limb leads are positioned on the arms and legs. The placement of these leads is as follows: - Lead I: The electrodes are placed on the inside of both arms, near the wrists. - Lead II: The electrodes are placed on the inside of the right arm and the inside of the left leg, near the ankle. - Lead III: The electrodes are placed on the inside of the left arm and the inside of the left leg, near the ankle. - aVR: The electrode is placed on the inside of the right arm, near the wrist. - aVL: The electrode is placed on the inside of the left arm, near the wrist. - aVF: The electrode is placed on the inside of the left leg, near the ankle.
Chest Leads Positioning
The chest leads are positioned on the chest, with specific locations for each lead: - V1: The electrode is placed on the right side of the chest, in the 4th intercostal space, near the sternum. - V2: The electrode is placed on the left side of the chest, in the 4th intercostal space, near the sternum. - V3: The electrode is placed midway between V2 and V4. - V4: The electrode is placed on the left side of the chest, in the 5th intercostal space, in the mid-clavicular line. - V5: The electrode is placed on the left side of the chest, in the 5th intercostal space, in the anterior axillary line. - V6: The electrode is placed on the left side of the chest, in the 5th intercostal space, in the mid-axillary line.
| Lead | Position |
|---|---|
| I | Inside of both arms, near the wrists |
| II | Inside of the right arm and the inside of the left leg, near the ankle |
| III | Inside of the left arm and the inside of the left leg, near the ankle |
| aVR | Inside of the right arm, near the wrist |
| aVL | Inside of the left arm, near the wrist |
| aVF | Inside of the left leg, near the ankle |
| V1 | Right side of the chest, in the 4th intercostal space, near the sternum |
| V2 | Left side of the chest, in the 4th intercostal space, near the sternum |
| V3 | Midway between V2 and V4 |
| V4 | Left side of the chest, in the 5th intercostal space, in the mid-clavicular line |
| V5 | Left side of the chest, in the 5th intercostal space, in the anterior axillary line |
| V6 | Left side of the chest, in the 5th intercostal space, in the mid-axillary line |

Importance of Correct ECG Lead Positioning

Correct positioning of the ECG leads is essential for several reasons: - Accurate Diagnosis: Incorrect lead placement can lead to inaccurate ECG readings, which may result in misdiagnosis and inappropriate treatment. - Reliable Monitoring: Correct lead placement ensures reliable monitoring of the heart’s electrical activity, which is critical in high-risk patients, such as those with cardiac arrhythmias or myocardial infarction. - Comparison with Previous Records: Accurate lead placement allows for comparison with previous ECG records, which is essential for monitoring changes in the heart’s electrical activity over time.
Pitfalls of Incorrect ECG Lead Positioning
Incorrect ECG lead positioning can lead to several pitfalls, including: - Inaccurate ECG Readings: Incorrect lead placement can result in inaccurate ECG readings, which may lead to misdiagnosis and inappropriate treatment. - Misinterpretation of ECG Findings: Incorrect lead placement can lead to misinterpretation of ECG findings, which may result in delayed or inappropriate treatment. - Decreased Sensitivity and Specificity: Incorrect lead placement can decrease the sensitivity and specificity of the ECG, making it less reliable for diagnostic purposes.
What is the purpose of the 12-lead ECG?
+The 12-lead ECG is used to record the electrical activity of the heart from 12 different views, providing a comprehensive assessment of the heart's electrical activity.
How often should ECG leads be checked for correct positioning?
+ECG leads should be checked for correct positioning before each ECG recording, and any adjustments should be made as needed to ensure accurate and reliable recordings.
In conclusion, correct positioning of ECG leads is crucial for obtaining reliable and interpretable ECG recordings. Understanding the importance of correct lead placement and the potential pitfalls of incorrect positioning can help healthcare professionals provide high-quality care and ensure accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.