Econ Automation: Simplifies Business Processes

The world of business is constantly evolving, with companies seeking innovative ways to streamline their operations, reduce costs, and enhance productivity. One significant development in this realm is the advent of econ automation, a technological solution designed to simplify business processes. By leveraging cutting-edge automation technologies, econ automation aims to revolutionize the way businesses operate, making them more efficient, agile, and competitive in the market. In this context, understanding the principles, applications, and implications of econ automation is crucial for businesses looking to stay ahead of the curve.
Introduction to Econ Automation

Econ automation refers to the use of automated systems and software to manage, execute, and optimize business processes. This includes a wide range of activities, from basic tasks such as data entry and document management to complex processes like financial analysis, supply chain management, and customer service. By automating these processes, businesses can significantly reduce manual labor, minimize errors, and increase the speed of execution, leading to improved overall performance and reduced operational costs. The key to successful econ automation lies in identifying the right processes to automate, understanding the technology requirements, and implementing these solutions in a way that complements existing business strategies.
Technologies Behind Econ Automation
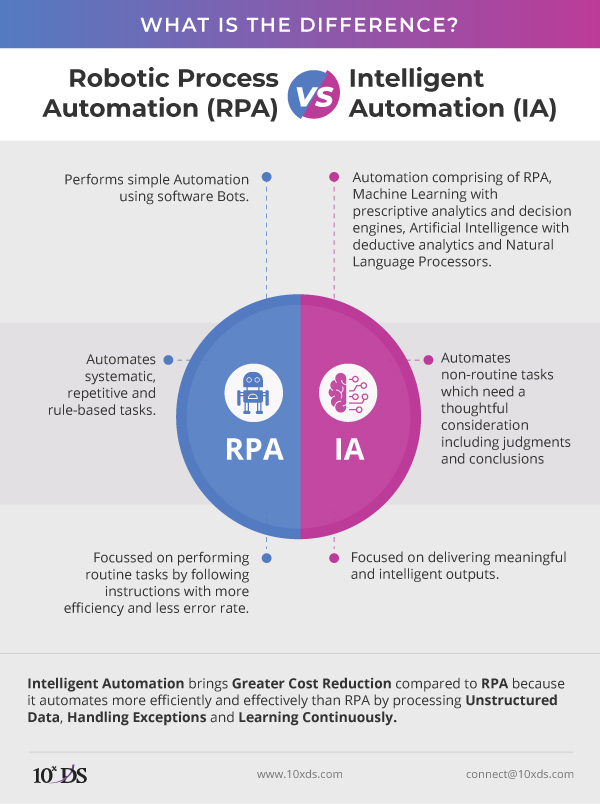
The foundation of econ automation is built upon several advanced technologies, including Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Robotic Process Automation (RPA). AI and ML enable systems to learn from data, make predictions, and improve process efficiency over time. RPA, on the other hand, allows for the automation of repetitive and rule-based tasks, freeing up human resources for more strategic and creative work. Additionally, cloud computing plays a crucial role by providing the infrastructure necessary for scalable, secure, and accessible automation solutions. The integration of these technologies enables businesses to automate complex processes that were previously thought to be too challenging or expensive to automate.
| Technology | Description | Application in Econ Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Enables machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence | Decision-making, predictive analytics, process optimization |
| Machine Learning (ML) | A subset of AI that involves training algorithms to learn from data | Predictive modeling, automation of complex processes, quality control |
| Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Software robots that can perform repetitive and rule-based tasks | Automation of back-office tasks, data entry, document processing |
Applications and Benefits of Econ Automation
The applications of econ automation are diverse and widespread, impacting various sectors and functions within an organization. From finance and accounting, where automated systems can handle transactions, invoicing, and compliance, to customer service, where chatbots and virtual assistants can provide 24⁄7 support, the potential for automation is vast. The benefits are equally compelling, including increased efficiency, reduced costs, enhanced customer experience, and improved compliance. By automating routine tasks, businesses can also free up resources for more strategic initiatives, fostering innovation and growth.
Case Studies and Examples
Several companies have already embraced econ automation, achieving significant improvements in their operations. For instance, a leading financial services firm used RPA to automate its account opening process, reducing the processing time from several days to just a few hours. Similarly, a retail company implemented an AI-powered chatbot to handle customer inquiries, resulting in a substantial decrease in customer support tickets and an increase in customer satisfaction ratings. These examples illustrate the practical applications and tangible benefits of econ automation in real-world scenarios.
- Automation of payroll processing in HR departments
- Use of AI in marketing for personalized customer engagement
- Implementation of automated inventory management in logistics and supply chain
What are the primary challenges in implementing econ automation?
+The primary challenges include identifying the right processes to automate, selecting the appropriate technology, ensuring data quality and security, and managing the change within the organization. Additionally, addressing potential job displacement and ensuring that automation complements human skills rather than replacing them is crucial.
How can businesses measure the success of econ automation initiatives?
+Success can be measured through various metrics, including reduction in processing times, decrease in error rates, increase in productivity, improvement in customer satisfaction, and return on investment (ROI). Regular monitoring and evaluation of these metrics can help in assessing the effectiveness of automation initiatives and in making necessary adjustments.
In conclusion, econ automation represents a significant leap forward in the quest for operational excellence and business efficiency. By understanding the technologies, applications, and benefits of econ automation, businesses can harness its potential to transform their operations, drive growth, and stay competitive in an ever-evolving market landscape. As the field continues to evolve, embracing innovation and leveraging the power of automation will be key to unlocking future success.
