Gmo Products Drawing Basics
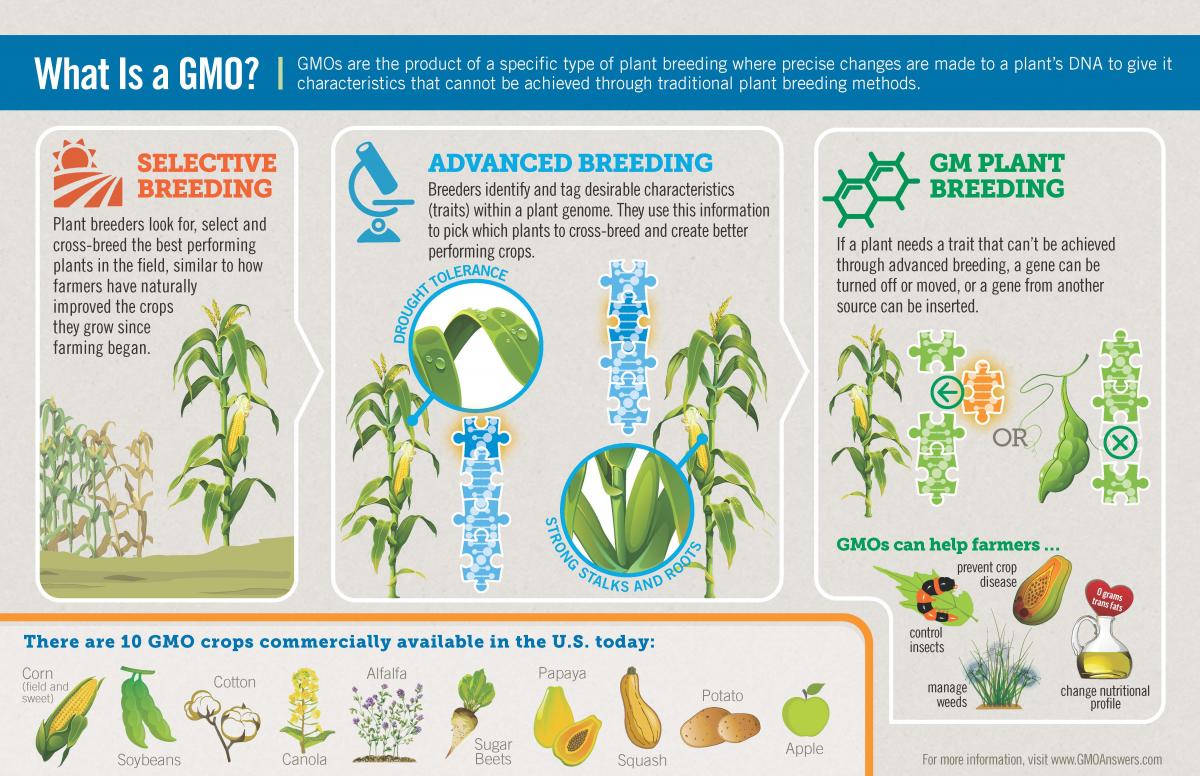
The creation and regulation of genetically modified organism (GMO) products have become a significant aspect of modern biotechnology, affecting various sectors such as agriculture, food production, and pharmaceuticals. Drawing the basics of GMO products involves understanding the fundamental concepts of genetic modification, its applications, and the ethical considerations surrounding its use. In this context, "drawing basics" refers to outlining the foundational principles and processes involved in the development and implementation of GMO products.
Introduction to Genetic Modification

Genetic modification is the process of altering an organism’s DNA to introduce new traits or characteristics. This can be achieved through various techniques, including the use of recombinant DNA technology, which allows for the insertion of genes from one species into the DNA of another. The goal of genetic modification can range from improving crop yields and resistance to pests and diseases, to producing pharmaceuticals and developing new biofuels.
Basics of GMO Production
The production of GMO products involves several key steps, including:
- Gene selection and cloning: Identifying and isolating the gene responsible for the desired trait and then cloning it to produce multiple copies.
- Vector construction: Creating a vector, such as a plasmid, to carry the cloned gene into the host organism.
- Transformation: Introducing the vector into the host organism, allowing the integration of the new gene into the organism’s genome.
- Selection and breeding: Selecting organisms that have successfully taken up the new gene and breeding them to produce offspring with the desired trait.
These steps are crucial in the development of GMO products, whether it be for agricultural use, such as corn and soybeans resistant to certain pests, or for medical applications, such as the production of insulin for diabetes treatment.
| Application | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Improving crop yields, disease resistance, and nutritional content | Golden Rice, Bt Corn |
| Pharmaceuticals | Producing drugs and vaccines | Insulin, Vaccines for Hepatitis B |
| Biotechnology | Developing new biofuels and bioproducts | Ethanol from genetically modified yeast, Biodegradable plastics |

Regulation and Safety Assessment

The regulation of GMO products is critical to ensure their safe use and to mitigate potential risks to human health and the environment. Regulatory agencies, such as the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), conduct thorough risk assessments before approving GMO products for market release. These assessments consider factors such as the potential for allergenicity, toxicity, and environmental impact.
Ethical Considerations and Public Perception
The development and use of GMO products also raise ethical considerations, including concerns about the patenting of life forms, the potential for genetic pollution, and the impact on biodiversity. Public perception of GMOs varies widely, with some viewing them as a crucial tool for addressing global food security and others expressing skepticism due to concerns about safety and the natural environment.
Understanding these ethical considerations and engaging in open dialogue with the public are essential for fostering trust and ensuring that the benefits of GMO products are realized while minimizing their risks.
What are the primary applications of GMO products?
+The primary applications of GMO products include agriculture, to improve crop yields and resistance to pests and diseases; pharmaceuticals, for the production of drugs and vaccines; and biotechnology, for the development of new biofuels and bioproducts.
How are GMO products regulated?
+GMO products are regulated by various national and international agencies, which conduct risk assessments to ensure their safety for human consumption and environmental release. These assessments consider factors such as potential allergenicity, toxicity, and environmental impact.
In conclusion, drawing the basics of GMO products requires a comprehensive understanding of genetic modification techniques, their applications, and the regulatory and ethical frameworks that govern their use. As technology continues to advance and the demand for sustainable and efficient solutions to global challenges grows, the role of GMO products is likely to become increasingly important.
