Horocycle Flow On Strata
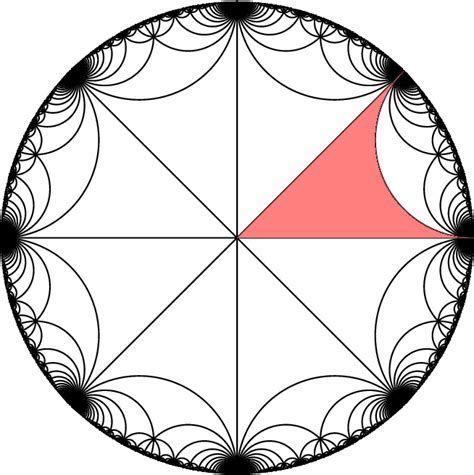
The horocycle flow on strata is a fundamental concept in the field of dynamical systems, particularly in the study of Teichmüller theory and the geometry of surfaces. The horocycle flow is a one-parameter group of transformations that acts on the unit tangent bundle of a hyperbolic surface, and its behavior is closely related to the properties of the surface. In this context, the term "strata" refers to the decomposition of the moduli space of curves into components based on the type of singularities present.
Introduction to Horocycle Flow
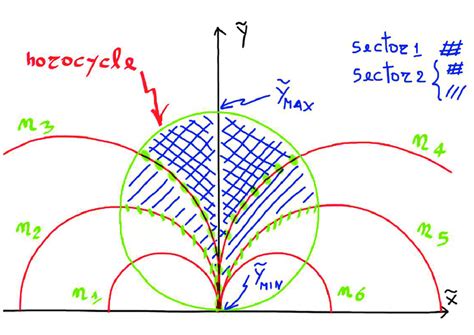
The horocycle flow is defined as the flow generated by the vector field X = \frac{\partial}{\partial x} + \frac{\partial}{\partial y} on the unit tangent bundle T^1S of a hyperbolic surface S. This flow is closely related to the geodesic flow, which is the flow generated by the vector field X = \frac{\partial}{\partial t}, where t is the parameter of the geodesic. The horocycle flow is a key tool in the study of the geometry and topology of hyperbolic surfaces, and its properties have important implications for our understanding of the moduli space of curves.
Properties of Horocycle Flow on Strata
The horocycle flow on strata has several important properties that are relevant to the study of Teichmüller theory. One key property is that the horocycle flow is ergodic, meaning that it is a measure-preserving transformation that is also mixing. This means that the flow has a strong tendency to “mix” the points of the surface, and that the time average of any measurable function will converge to its space average. Another important property is that the horocycle flow is uniquely ergodic, meaning that there is a unique invariant measure for the flow. This measure is known as the Lebesgue measure, and it plays a central role in the study of the horocycle flow.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Ergodicity | The horocycle flow is a measure-preserving transformation that is also mixing. |
| Unique Ergodicity | There is a unique invariant measure for the horocycle flow, known as the Lebesgue measure. |
| Topological Transitivity | The horocycle flow is topologically transitive, meaning that for any two open sets, there exists a time $t$ such that the flow maps one set into the other. |

Applications of Horocycle Flow on Strata

The horocycle flow on strata has several important applications in the study of Teichmüller theory and the geometry of surfaces. One key application is in the study of the Teichmüller metric, which is a metric on the moduli space of curves that is defined in terms of the distance between two curves. The horocycle flow is used to study the properties of this metric, and its behavior has important implications for our understanding of the geometry of the moduli space. Another important application is in the study of the intersection theory of curves, which is a way of studying the properties of curves by looking at their intersections with other curves.
Technical Specifications
The technical specifications of the horocycle flow on strata are based on the properties of the flow and the geometry of the surface. The flow is defined as a one-parameter group of transformations, and its behavior is closely related to the properties of the surface. The curvature of the surface plays a key role in the behavior of the flow, and the topology of the surface also has important implications for the properties of the flow.
- The horocycle flow is a one-parameter group of transformations that acts on the unit tangent bundle of a hyperbolic surface.
- The flow is defined in terms of the vector field $X = \frac{\partial}{\partial x} + \frac{\partial}{\partial y}$.
- The flow is closely related to the geodesic flow, which is the flow generated by the vector field $X = \frac{\partial}{\partial t}$.
What is the relationship between the horocycle flow and the Teichmüller metric?
+The horocycle flow is used to study the properties of the Teichmüller metric, which is a metric on the moduli space of curves that is defined in terms of the distance between two curves. The behavior of the horocycle flow has important implications for our understanding of the geometry of the moduli space.
How does the curvature of the surface affect the behavior of the horocycle flow?
+The curvature of the surface plays a key role in the behavior of the horocycle flow. The flow is defined in terms of the vector field X = \frac{\partial}{\partial x} + \frac{\partial}{\partial y}, and the curvature of the surface affects the properties of this vector field. The Gaussian curvature of the surface is particularly important, as it determines the rate at which the flow diverges or converges.