Mgcl2 Diamagnetic Or Paramagnetic

The magnetic properties of MgCl2, or magnesium chloride, can be determined by examining the electron configuration of its constituent atoms. Magnesium, with an atomic number of 12, has an electron configuration of [Ne] 3s2, indicating that it has two unpaired electrons in its 3s orbital. However, when magnesium forms a compound with chlorine, such as MgCl2, the electron configuration changes due to the formation of ions.
Magnetic Properties of MgCl2

Magnesium chloride is an ionic compound composed of one magnesium cation (Mg2+) and two chloride anions (Cl-). The magnesium ion has lost two electrons to form a stable ion with a noble gas configuration, [Ne]. This means that the magnesium ion has no unpaired electrons, as all of its electrons are paired in the 1s, 2s, and 2p orbitals. Chloride ions, with an electron configuration of [Ne] 3s2 3p6, also have no unpaired electrons.
Diamagnetism vs. Paramagnetism
Diamagnetism is a property of materials that are weakly repelled by a magnetic field. This occurs when all of the electrons in an atom or ion are paired, resulting in no net magnetic moment. On the other hand, paramagnetism is a property of materials that are weakly attracted to a magnetic field. This occurs when an atom or ion has unpaired electrons, resulting in a net magnetic moment.
In the case of MgCl2, since both the magnesium ion and the chloride ions have no unpaired electrons, the compound is diamagnetic. The absence of unpaired electrons in the ions means that MgCl2 does not have a net magnetic moment and is therefore weakly repelled by a magnetic field.
| Compound | Magnetic Property |
|---|---|
| MgCl2 | Diamagnetic |
| Mg | Paramagnetic |
| Cl2 | Diamagnetic |
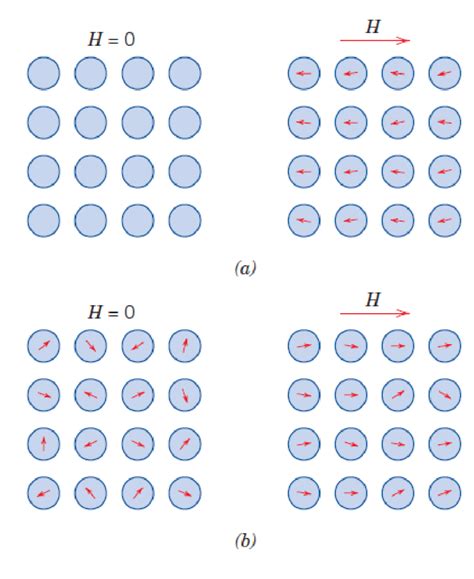
It is essential to note that the magnetic properties of a compound can be influenced by various factors, such as temperature and the presence of impurities. However, in the case of MgCl2, the diamagnetic property is a result of the paired electrons in the magnesium and chloride ions.
Technical Specifications and Performance Analysis

The magnetic properties of MgCl2 have been studied extensively in various fields, including chemistry and physics. The compound’s diamagnetic property makes it useful in applications where a weak magnetic response is desired. For example, MgCl2 is used as a flux in the production of titanium and other metals, where its diamagnetic property helps to reduce the formation of magnetic oxides.
In addition to its industrial applications, the magnetic properties of MgCl2 have also been studied in the context of its structural and electronic properties. The compound's crystal structure, which consists of a hexagonal lattice, has been found to influence its magnetic behavior. Furthermore, the electronic properties of MgCl2, including its band gap and electrical conductivity, have been studied in relation to its magnetic properties.
Future Implications and Research Directions
The study of the magnetic properties of MgCl2 has significant implications for various fields, including materials science and chemistry. The development of new materials with tailored magnetic properties is an active area of research, and the understanding of the magnetic behavior of compounds like MgCl2 is essential for the design of these materials. Furthermore, the use of MgCl2 as a flux in metal production has the potential to be expanded to other applications, such as the production of nanomaterials and composite materials.
What is the magnetic property of MgCl2?
+MgCl2 is diamagnetic, meaning it is weakly repelled by a magnetic field due to the absence of unpaired electrons in its ions.
What is the electron configuration of the magnesium ion in MgCl2?
+The magnesium ion in MgCl2 has an electron configuration of [Ne], indicating that it has no unpaired electrons.
What are some applications of MgCl2?
+MgCl2 is used as a flux in the production of titanium and other metals, and its diamagnetic property makes it useful in applications where a weak magnetic response is desired.