Microfluidic Dep Printing Mastery
Microfluidic dep printing, also known as microfluidic deposition printing, is a cutting-edge technology that has revolutionized the field of additive manufacturing. This innovative technique enables the creation of complex, three-dimensional structures with unprecedented precision and accuracy. By combining microfluidics and 3D printing, researchers and engineers can fabricate intricate devices and systems with unique properties, such as microfluidic channels, valves, and pumps. In this article, we will delve into the world of microfluidic dep printing, exploring its fundamentals, applications, and future implications.
Principles of Microfluidic Dep Printing

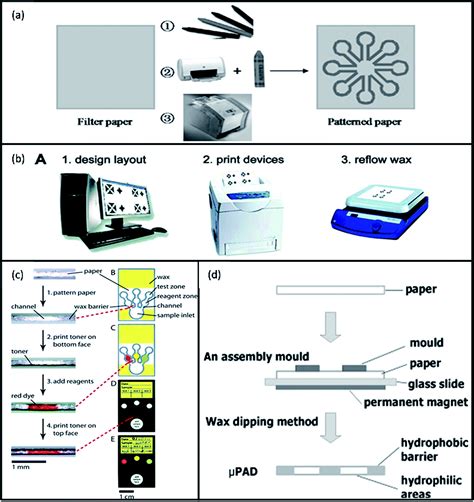
Microfluidic dep printing is based on the principle of depositing tiny droplets of fluid onto a substrate, which are then solidified to form a three-dimensional structure. This process involves the use of microfluidic devices, which are designed to manipulate and control the flow of fluids at the microscale. The deposition process is typically achieved through a combination of pneumatic, thermal, or electrical actuation mechanisms. By carefully controlling the flow rate, viscosity, and surface tension of the fluid, researchers can create complex geometries and patterns with high spatial resolution.
Key Components of Microfluidic Dep Printing
A typical microfluidic dep printing system consists of several key components, including a fluid reservoir, a pump, a microfluidic chip, and a printing head. The fluid reservoir stores the printing material, which can be a polymer, ceramic, or metal suspension. The pump generates the pressure required to drive the fluid through the microfluidic chip, which is designed to control the flow rate and direction of the fluid. The printing head is responsible for depositing the fluid onto the substrate, where it solidifies to form the final structure.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Fluid Reservoir | Stores the printing material |
| Pump | Generates pressure to drive the fluid |
| Microfluidic Chip | Controls the flow rate and direction of the fluid |
| Printing Head | Deposits the fluid onto the substrate |
Applications of Microfluidic Dep Printing
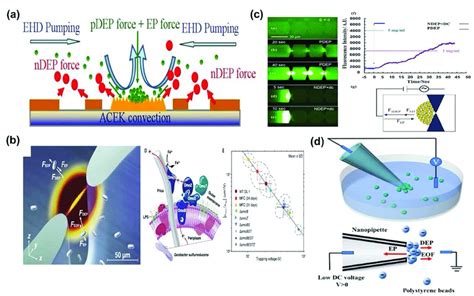
Microfluidic dep printing has a wide range of applications across various fields, including biomedical engineering, energy storage, and optics. In biomedical engineering, microfluidic dep printing can be used to create complex tissue engineering scaffolds, biosensors, and implantable devices. In energy storage, microfluidic dep printing can be used to fabricate advanced battery architectures and supercapacitors. In optics, microfluidic dep printing can be used to create complex optical devices, such as lenses, waveguides, and optical fibers.
Biomedical Applications
In the biomedical field, microfluidic dep printing has been used to create complex tissue engineering scaffolds, which can be used to repair or replace damaged tissues. For example, researchers have used microfluidic dep printing to create scaffolds for bone tissue engineering, which can be used to repair bone defects. Microfluidic dep printing has also been used to create biosensors, which can be used to detect biomarkers for diseases such as cancer and diabetes.
- Tissue engineering scaffolds
- Biosensors
- Implantable devices
What is the resolution of microfluidic dep printing?
+The resolution of microfluidic dep printing can range from tens of micrometers to several millimeters, depending on the specific application and the design of the microfluidic chip.
What types of materials can be used in microfluidic dep printing?
+A wide range of materials can be used in microfluidic dep printing, including polymers, ceramics, metals, and biomaterials.
Future Implications of Microfluidic Dep Printing

Microfluidic dep printing has the potential to revolutionize various fields, including biomedical engineering, energy storage, and optics. As the technology continues to advance, we can expect to see the development of more complex and sophisticated devices and systems. For example, microfluidic dep printing could be used to create implantable devices that can monitor and treat diseases in real-time. Additionally, microfluidic dep printing could be used to create advanced energy storage systems, such as batteries and supercapacitors, which could enable the widespread adoption of electric vehicles and renewable energy sources.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the many advantages of microfluidic dep printing, there are several challenges and limitations that need to be addressed. One of the main challenges is the need for high-resolution printing, which requires the development of advanced microfluidic chips and printing heads. Another challenge is the need for biocompatibility and biostability, which is critical for biomedical applications. Finally, there is a need for standardized protocols and regulations, which would enable the widespread adoption of microfluidic dep printing in various industries.