Migraine On Dolorimeter Scae
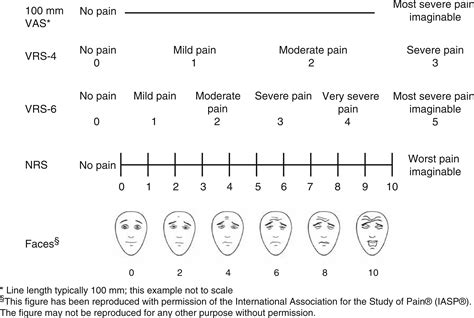
Migraine is a complex and debilitating neurological disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of severe headaches, often accompanied by sensitivity to light, sound, and nausea. The Dolorimeter Scale, a tool used to measure pain intensity, is frequently employed in clinical settings to assess the severity of migraine headaches. Understanding the relationship between migraine and the Dolorimeter Scale is essential for effective diagnosis, treatment, and management of this condition.
Migraine Pathophysiology and Pain Measurement
Migraine pathophysiology involves a multifaceted interplay of vascular, neuronal, and hormonal factors. The exact mechanisms underlying migraine pain are not fully understood, but it is believed that activation of trigeminal nerves plays a critical role, leading to the release of various neurotransmitters and the dilation of blood vessels. The Dolorimeter Scale, which ranges from 0 to 10, with 0 indicating no pain and 10 representing the worst possible pain, provides a subjective measure of pain intensity. In the context of migraine, patients often report pain levels ranging from 6 to 10 on the Dolorimeter Scale during an episode.
Pain Assessment and Migraine Diagnosis
Accurate pain assessment is crucial for the diagnosis and management of migraine. Healthcare providers use the Dolorimeter Scale, along with other diagnostic criteria such as the International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD), to determine the severity and frequency of migraine episodes. The scale helps in differentiating migraine from other types of headaches, such as tension-type headaches, which typically score lower on the Dolorimeter Scale. Furthermore, tracking changes in pain intensity over time can aid in evaluating the effectiveness of treatment strategies.
| Pain Intensity | Dolorimeter Scale | Migraine Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Mild | 1-3 | Infrequent episodes, minimal impact on daily activities |
| Moderate | 4-6 | Frequent episodes, some impact on daily activities, may require medication |
| Severe | 7-10 | Frequent and debilitating episodes, significant impact on daily activities, often requires aggressive treatment |

Treatment Strategies for Migraine

Treatment of migraine involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, preventive medications, and acute therapies. Lifestyle changes include avoiding triggers, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, and engaging in regular physical activity. Preventive medications, such as topiramate and propranolol, are used to reduce the frequency and severity of migraine episodes. Acute therapies, including triptans and ergots, are administered to alleviate symptoms during an episode. The choice of treatment is influenced by the patient’s medical history, the severity of migraine episodes as indicated by the Dolorimeter Scale, and the presence of any comorbid conditions.
Emerging Therapies for Migraine
Recent advances in the field of migraine research have led to the development of new therapeutic options. These include calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) inhibitors, which have shown significant promise in reducing the frequency of migraine episodes. Other emerging therapies, such as non-invasive neuromodulation techniques, offer potential for the treatment of acute migraine attacks. As research continues to uncover the complexities of migraine pathophysiology, it is likely that more targeted and effective treatments will become available, potentially leading to improved outcomes for patients and a reduction in the societal burden of migraine.
- Identifying and avoiding migraine triggers
- Implementing stress management techniques, such as meditation and yoga
- Engaging in regular physical activity to improve overall health and reduce migraine frequency
What is the role of the Dolorimeter Scale in migraine diagnosis?
+The Dolorimeter Scale provides a subjective measure of pain intensity, aiding healthcare providers in assessing the severity of migraine episodes and differentiating migraine from other types of headaches.
How does the severity of migraine, as measured by the Dolorimeter Scale, influence treatment choices?
+The severity of migraine, as indicated by the Dolorimeter Scale, plays a significant role in guiding treatment decisions. Patients with more severe migraine episodes may require more aggressive treatment strategies, including preventive medications and acute therapies.
In conclusion, the relationship between migraine and the Dolorimeter Scale is a critical aspect of migraine diagnosis and management. By understanding the complexities of migraine pathophysiology and the role of pain measurement in clinical practice, healthcare providers can develop personalized treatment plans that address the unique needs of each patient, ultimately leading to improved outcomes and a reduction in the societal burden of migraine.
