Nuclear Annihilation: Reduce Radiation Exposure

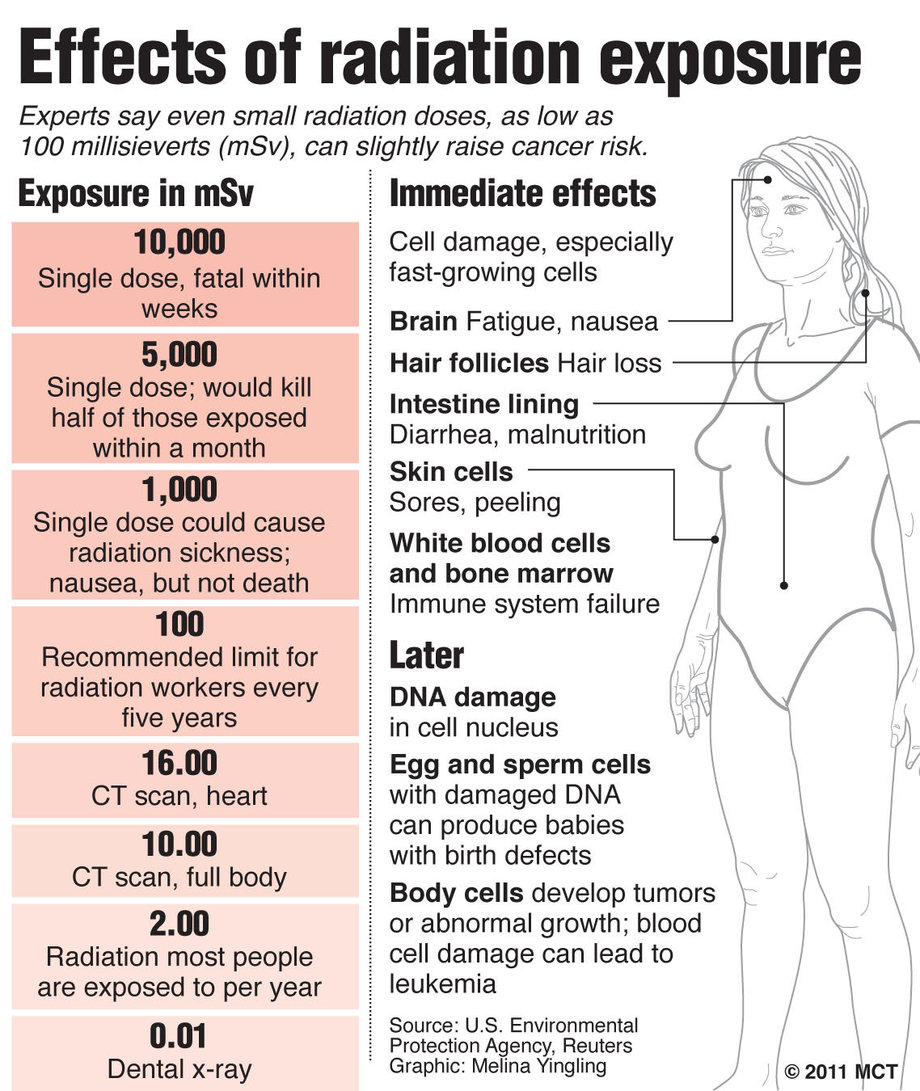
Nuclear annihilation poses a significant threat to human life and the environment, with radiation exposure being a major concern. In the event of a nuclear disaster, it is crucial to understand the risks associated with radiation and take necessary precautions to minimize exposure. Radiation can cause severe health problems, including cancer, genetic mutations, and damage to the central nervous system. The effects of radiation exposure can be immediate or delayed, depending on the dose and duration of exposure. In this context, reducing radiation exposure is essential to prevent long-term health consequences and save lives.
Understanding Radiation Exposure

Radiation exposure occurs when an individual comes into contact with radioactive materials, such as radioactive isotopes or nuclear fallout. The level of exposure depends on various factors, including the type and amount of radioactive material, the duration of exposure, and the distance from the source. Alpha, beta, and gamma radiation are the three main types of radiation, each with distinct properties and effects on human health. Alpha radiation is the most harmful, as it can cause significant damage to living tissues, while beta and gamma radiation are less harmful but can still cause significant health problems. Radiation sickness is a condition that occurs when an individual is exposed to high levels of radiation, causing symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fatigue.
Reducing Radiation Exposure
To reduce radiation exposure, it is essential to take a multi-faceted approach that includes prevention, protection, and mitigation. Prevention involves avoiding areas with high levels of radiation, while protection involves using personal protective equipment (PPE) such as masks, gloves, and suits. Mitigation involves reducing the amount of radioactive material in the environment through decontamination and remediation efforts. Sheltering is also an effective way to reduce radiation exposure, as it provides a physical barrier between the individual and the radioactive material. In addition, potassium iodide can be used to prevent the uptake of radioactive iodine by the thyroid gland, reducing the risk of thyroid cancer.
| Radiation Type | Effects on Human Health |
|---|---|
| Alpha Radiation | Causes significant damage to living tissues, leading to cancer and genetic mutations |
| Beta Radiation | Causes less harm than alpha radiation, but can still cause significant health problems, including cancer and radiation sickness |
| Gamma Radiation | Causes less harm than alpha and beta radiation, but can still cause significant health problems, including cancer and radiation sickness |
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)

PPE is a critical component of reducing radiation exposure, as it provides a physical barrier between the individual and the radioactive material. Masks, gloves, and suits are common types of PPE used to prevent radiation exposure. Masks can filter out radioactive particles, while gloves and suits can prevent skin contact with radioactive materials. Respirators are also used to prevent inhalation of radioactive particles, providing an additional layer of protection. When selecting PPE, it is essential to consider the type and level of radiation exposure, as well as the individual’s specific needs and requirements.
Decontamination and Remediation
Decontamination and remediation are critical steps in reducing radiation exposure, as they involve removing or reducing the amount of radioactive material in the environment. Decontamination involves removing radioactive material from surfaces, while remediation involves reducing the amount of radioactive material in the environment through techniques such as excavation and removal. Phytoremediation is a technique that uses plants to remove radioactive material from the soil, providing a natural and effective solution. In addition, radiation monitoring is essential to track the levels of radiation and ensure that decontamination and remediation efforts are effective.
- Decontamination techniques include washing, scrubbing, and vacuuming surfaces to remove radioactive material
- Remediation techniques include excavation, removal, and phytoremediation to reduce the amount of radioactive material in the environment
- Radiation monitoring involves tracking the levels of radiation to ensure that decontamination and remediation efforts are effective
What are the effects of radiation exposure on human health?
+Radiation exposure can cause severe health problems, including cancer, genetic mutations, and damage to the central nervous system. The effects of radiation exposure can be immediate or delayed, depending on the dose and duration of exposure.
How can I reduce radiation exposure?
+To reduce radiation exposure, it is essential to take a multi-faceted approach that includes prevention, protection, and mitigation. This includes avoiding areas with high levels of radiation, using personal protective equipment, and reducing the amount of radioactive material in the environment through decontamination and remediation efforts.
What is the role of potassium iodide in reducing radiation exposure?
+Potassium iodide can be used to prevent the uptake of radioactive iodine by the thyroid gland, reducing the risk of thyroid cancer. It is essential to note that potassium iodide is not a substitute for other forms of protection, such as sheltering and personal protective equipment.
In conclusion, reducing radiation exposure is essential to prevent long-term health consequences and save lives. By understanding the risks associated with radiation and taking necessary precautions, individuals can minimize their exposure and reduce the risk of severe health problems. It is crucial to take a multi-faceted approach that includes prevention, protection, and mitigation, and to use personal protective equipment, decontamination, and remediation techniques to reduce the amount of radioactive material in the environment. By working together, we can reduce the risks associated with radiation exposure and create a safer and healthier environment for everyone.