Phq9 And Gad7 Pdf

The Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7-item scale (GAD-7) are two widely used screening tools in the field of mental health. These tools are designed to assess the severity of symptoms of depression and anxiety, respectively, in patients. Both the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 are utilized by healthcare professionals to monitor the progression of symptoms over time, evaluate the effectiveness of treatments, and facilitate communication between patients and healthcare providers.
Introduction to PHQ-9 and GAD-7

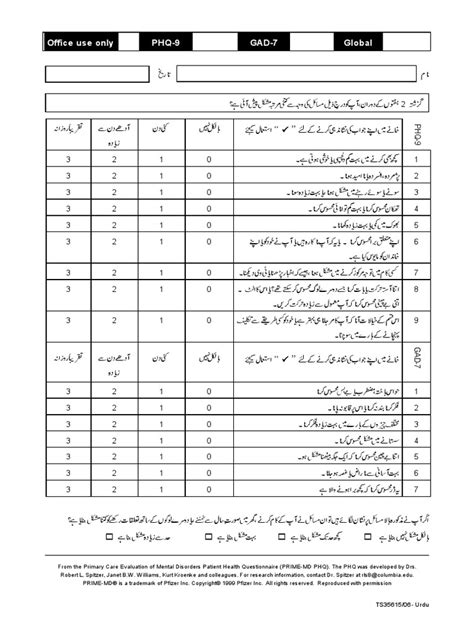
The PHQ-9 is a 9-item instrument that assesses the frequency of depressive symptoms over the past two weeks. It is based on the diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder as defined by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition (DSM-IV). Each item on the PHQ-9 is scored from 0 to 3, with higher scores indicating more severe symptoms. The total score ranges from 0 to 27, allowing for the categorization of depression severity into five levels: none (0-4), mild (5-9), moderate (10-14), moderately severe (15-19), and severe (20-27).
The GAD-7, on the other hand, is a 7-item scale used to assess the severity of anxiety symptoms. Similar to the PHQ-9, each item is scored from 0 to 3, with the total score ranging from 0 to 21. The severity of anxiety can be categorized into four levels based on the total score: none (0-4), mild (5-9), moderate (10-14), and severe (15-21). Both the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 are self-report instruments, meaning patients complete them independently, which facilitates their use in various clinical settings.
Administration and Scoring
The administration of both the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 is straightforward. Patients are asked to complete the questionnaires based on their experiences over the past two weeks. The scoring process involves summing the scores of each item. For both tools, higher scores indicate more severe symptoms. The simplicity and brevity of these instruments make them practical for use in busy clinical environments, where time and resources may be limited.
The following table illustrates the scoring guidelines for the PHQ-9 and GAD-7:
| Instrument | Score Range | Severity Level |
|---|---|---|
| PHQ-9 | 0-4 | |
| PHQ-9 | 5-9 | Mild |
| PHQ-9 | 10-14 | Moderate |
| PHQ-9 | 15-19 | Moderately Severe |
| PHQ-9 | 20-27 | Severe |
| GAD-7 | 0-4 | |
| GAD-7 | 5-9 | Mild |
| GAD-7 | 10-14 | Moderate |
| GAD-7 | 15-21 | Severe |
Clinical Utility and Limitations

Both the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 have been validated for use in primary care and mental health settings. They are valuable for identifying patients who may require a more comprehensive diagnostic evaluation or for monitoring treatment response. However, it is essential to recognize that these tools are screening instruments and not diagnostic tools. A comprehensive diagnostic assessment by a qualified healthcare professional is necessary for an accurate diagnosis of depression or anxiety disorders.
Despite their utility, the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 have limitations. They are subject to patient self-report bias, and scores can be influenced by the patient's understanding of the questions, their willingness to disclose symptoms, and their current mental state. Additionally, these instruments may not capture the full complexity of an individual's experience with depression or anxiety, as they focus on symptom severity rather than the broader impact of these conditions on daily life and functioning.
Future Directions and Implications
The widespread adoption of the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 in clinical practice underscores their value in mental health care. Future research should continue to evaluate and refine these instruments to improve their sensitivity and specificity. Moreover, integrating these tools into electronic health records and leveraging technology to facilitate their administration and scoring could enhance their utility and accessibility in diverse clinical settings.
The implications of the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 extend beyond clinical practice. They contribute to public health efforts aimed at reducing the burden of mental illness. By facilitating early identification and treatment of depression and anxiety, these tools can help mitigate the adverse effects of these conditions on individuals, families, and communities.
What is the primary use of the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 in clinical practice?
+The primary use of the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 is to screen for and monitor the severity of depressive and anxiety symptoms, respectively, in patients. These tools help healthcare providers identify individuals who may require further diagnostic evaluation or treatment and monitor the effectiveness of interventions over time.
Can the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 be used as diagnostic tools?
+No, the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 are screening instruments, not diagnostic tools. While they can indicate the presence and severity of depressive and anxiety symptoms, a comprehensive diagnostic evaluation by a qualified healthcare professional is necessary for an accurate diagnosis of depression or anxiety disorders.