Proton Exchange: Boosts Energy Efficiency

The concept of proton exchange has been gaining significant attention in recent years due to its potential to boost energy efficiency in various industrial processes. At its core, proton exchange refers to the process of exchanging protons (hydrogen ions) between two substances, often with the goal of generating energy or enhancing chemical reactions. This process is particularly relevant in the context of fuel cells, where it plays a crucial role in converting chemical energy into electrical energy. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of proton exchange, its mechanisms, and its applications, with a focus on how it enhances energy efficiency.
Principles of Proton Exchange
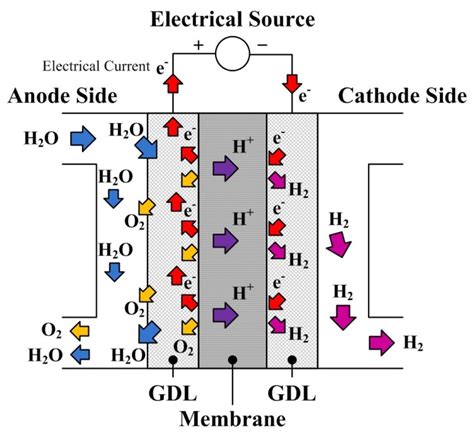
Proton exchange is fundamentally a chemical process that involves the transfer of protons from one molecule to another. This transfer is facilitated by a medium, often a polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM), which selectively allows protons to pass through while blocking the flow of electrons. The most common application of this principle is in proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs), where hydrogen fuel is oxidized at the anode, releasing protons and electrons. The protons then migrate through the PEM to the cathode, where they combine with oxygen and the electrons (that have traveled through an external circuit) to form water, thus generating electricity.
Proton Exchange Membranes (PEMs)
PEMs are a critical component in proton exchange systems, particularly in fuel cells. These membranes are designed to be highly selective, allowing protons to pass through while preventing the crossover of reactants and products, which would reduce the efficiency of the cell. The most widely used PEMs are based on perfluorosulfonic acid (PFSA) polymers, such as Nafion. However, research is ongoing to develop new membrane materials that offer improved proton conductivity, reduced gas permeability, and enhanced durability, all of which are key factors in boosting energy efficiency.
| Property | Value for Nafion |
|---|---|
| Proton Conductivity | 0.1 S/cm |
| Water Uptake | 30-40% |
| Thickness | 50-200 μm |

Applications and Energy Efficiency

The applications of proton exchange are diverse, ranging from fuel cells in electric vehicles and stationary power generation to electrochemical synthesis and water treatment. In each of these applications, the efficiency of proton exchange directly influences the overall performance and energy output. For instance, in fuel cells, higher proton conductivity and more efficient proton exchange lead to higher power densities and lower energy losses, thereby boosting energy efficiency.
Enhancing Energy Efficiency
Several strategies are being explored to enhance the energy efficiency of proton exchange systems. These include the development of more efficient PEMs, as mentioned earlier, as well as innovations in electrode design, catalysts, and operating conditions. For example, the use of nanostructured electrodes can increase the surface area available for reactions, thereby enhancing proton exchange rates and reducing energy losses. Similarly, optimizing the operating temperature and humidity levels can significantly impact the proton conductivity of the PEM and the overall efficiency of the system.
Furthermore, the integration of proton exchange systems with other technologies, such as solar panels or wind turbines, can create highly efficient hybrid systems that maximize energy output while minimizing losses. Such hybrid approaches are particularly promising for stationary power generation and grid-scale energy storage applications.
- Improved PEM materials for higher proton conductivity
- Optimized electrode design for increased surface area and reaction rates
- Advanced catalysts for reduced energy losses and improved efficiency
- Hybrid systems integrating proton exchange with renewable energy sources
What is the primary challenge in developing more efficient proton exchange membranes?
+The primary challenge is achieving a balance between high proton conductivity and low gas permeability, along with ensuring durability and stability under operating conditions.
How does proton exchange impact energy efficiency in fuel cells?
+Proton exchange directly influences the efficiency of fuel cells by affecting the rate of chemical reactions and the flow of electrical current. More efficient proton exchange leads to higher power densities and lower energy losses.
In conclusion, proton exchange is a critical process that underpins various energy conversion and storage technologies, with significant implications for energy efficiency. Ongoing research and development in this area, particularly in the design of proton exchange membranes and the optimization of operating conditions, are poised to further enhance the efficiency and applicability of these systems. As the world transitions towards more sustainable and efficient energy solutions, the role of proton exchange is likely to become increasingly prominent.
