Quantized Probability Density Functions
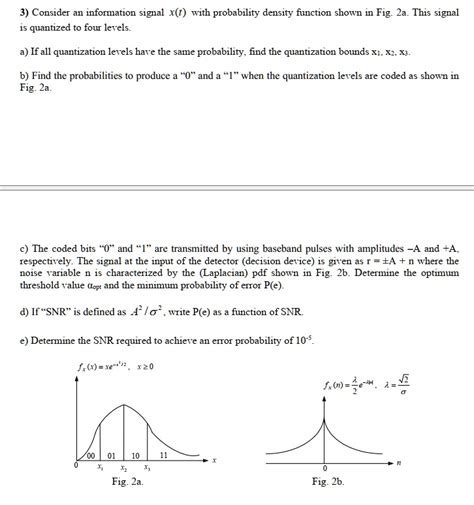
Quantized probability density functions (PDFs) are a fundamental concept in probability theory and information theory, playing a crucial role in various fields such as signal processing, communication systems, and machine learning. The quantization of a continuous PDF involves approximating it using a finite number of discrete values, which can significantly simplify the analysis and processing of random variables. In this article, we will delve into the world of quantized PDFs, exploring their definition, properties, and applications.
Definition and Properties

A quantized PDF is obtained by partitioning the range of a continuous random variable into a finite number of intervals, called quantization bins or cells. Each bin is associated with a discrete value, which represents the approximate value of the random variable within that interval. The probability of each bin is calculated as the integral of the original PDF over the corresponding interval. The resulting quantized PDF is a discrete probability distribution, which can be represented as a set of pairs, where each pair consists of a discrete value and its corresponding probability.
The quantization error is a critical aspect of quantized PDFs, as it measures the difference between the original continuous PDF and its quantized approximation. The quantization error can be minimized by optimizing the quantization bins and the discrete values associated with each bin. Entropy, a fundamental concept in information theory, is often used to quantify the amount of information lost due to quantization. The entropy rate of a quantized PDF is a measure of the average amount of information lost per sample, and it can be used to evaluate the trade-off between the accuracy of the quantized PDF and the number of quantization bins.
Types of Quantization
There are several types of quantization techniques, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Uniform quantization is a simple and widely used technique, where the quantization bins are evenly spaced and have the same width. Non-uniform quantization techniques, such as Lloyd-Max quantization, can provide better performance by adapting the quantization bins to the shape of the underlying PDF. Entropy-constrained quantization is another technique that optimizes the quantization bins to minimize the entropy rate, subject to a constraint on the number of quantization bins.
| Quantization Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Uniform Quantization | Evenly spaced quantization bins with the same width |
| Non-Uniform Quantization | Quantization bins adapted to the shape of the underlying PDF |
| Entropy-Constrained Quantization | Optimization of quantization bins to minimize entropy rate subject to a constraint |

Applications of Quantized PDFs
Quantized PDFs have numerous applications in various fields, including signal processing, communication systems, and machine learning. In signal processing, quantized PDFs are used to model and analyze discrete-time signals, such as audio and image signals. In communication systems, quantized PDFs are used to design and optimize communication protocols, such as source coding and channel coding. In machine learning, quantized PDFs are used to model and analyze complex data distributions, such as those encountered in natural language processing and computer vision.
The discrete cosine transform (DCT) is a widely used technique in signal processing that relies on quantized PDFs. The DCT is a linear transformation that represents a discrete-time signal in the frequency domain, and it is often used in conjunction with quantized PDFs to compress and reconstruct signals. Vector quantization is another technique that uses quantized PDFs to compress and reconstruct high-dimensional data, such as images and videos.
Performance Analysis
The performance of quantized PDFs can be evaluated using various metrics, such as the mean squared error (MSE) and the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR). The MSE measures the average squared difference between the original signal and its quantized approximation, while the PSNR measures the ratio of the maximum possible power of a signal to the power of the quantization error. Rate-distortion theory provides a framework for analyzing the trade-off between the rate of a quantized PDF and its distortion, which is a measure of the difference between the original signal and its quantized approximation.
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Mean Squared Error (MSE) | Average squared difference between the original signal and its quantized approximation |
| Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) | Ratio of the maximum possible power of a signal to the power of the quantization error |
| Rate-Distortion Theory | Framework for analyzing the trade-off between the rate of a quantized PDF and its distortion |
Future Implications
The study of quantized PDFs has significant implications for the development of future technologies, such as 5G communication systems and artificial intelligence. The increasing demand for high-speed and low-latency communication systems requires the development of more efficient quantization techniques, which can provide better performance and lower complexity. Additionally, the growing need for machine learning and artificial intelligence applications requires the development of more advanced quantization techniques, which can handle complex data distributions and provide better performance.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is another area where quantized PDFs can play a crucial role. The IoT involves the connection of a large number of devices, such as sensors and actuators, which can generate a vast amount of data. Quantized PDFs can be used to model and analyze this data, providing insights into the behavior of the devices and the underlying systems. Edge computing is a technique that can be used to process and analyze the data generated by the IoT devices, reducing the latency and improving the performance of the system.
What is the main advantage of quantized PDFs?
+The main advantage of quantized PDFs is that they can simplify the analysis and processing of random variables, making it possible to model and analyze complex systems using discrete probability distributions.
What is the difference between uniform and non-uniform quantization?
+Uniform quantization involves dividing the range of a continuous random variable into evenly spaced intervals, while non-uniform quantization involves adapting the quantization bins to the shape of the underlying PDF.
What is the role of entropy in quantized PDFs?
+Entropy is a measure of the amount of information lost due to quantization, and it can be used to evaluate the trade-off between the accuracy of the quantized PDF and the number of quantization bins.