Radio Stations Change Antenna Polarization
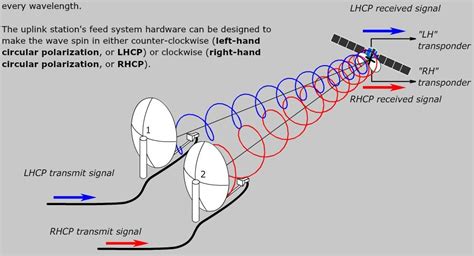
The world of radio broadcasting has witnessed significant transformations over the years, with one of the notable changes being the shift in antenna polarization. Antenna polarization refers to the orientation of the electric field vector of a radio wave as it radiates from the antenna. The two primary types of polarization are horizontal and vertical, with circular polarization being a combination of both. The choice of polarization depends on various factors, including the intended coverage area, terrain, and the type of radio service being provided.
History of Antenna Polarization in Radio Broadcasting

Historically, most radio stations used vertical polarization for their antennas, as it was believed to provide better coverage and penetration into buildings. However, with the advent of new technologies and a better understanding of radio wave propagation, many stations have started to adopt horizontal polarization or a combination of both. This shift has been driven by the need to improve signal quality, reduce interference, and increase the efficiency of radio transmissions. Polarization diversity has become a key concept in modern radio broadcasting, allowing stations to transmit signals with multiple polarization modes to cater to different reception scenarios.
Benefits of Changing Antenna Polarization
Changing antenna polarization can bring several benefits to radio stations, including improved signal-to-noise ratio, reduced multipath effects, and increased coverage area. By switching to horizontal polarization, stations can take advantage of the fact that horizontal signals tend to travel farther and penetrate vegetation more easily. This is particularly useful for stations broadcasting in areas with dense foliage or hilly terrain. Additionally, horizontal polarization can help reduce interference from other radio stations, allowing for a cleaner signal and better listener experience.
| Type of Polarization | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Vertical Polarization | Better penetration into buildings, more suitable for urban areas |
| Horizontal Polarization | Farther signal travel, easier penetration of vegetation, more suitable for rural areas |
| Circular Polarization | Combination of vertical and horizontal polarization, provides polarization diversity and improved signal quality |

Challenges and Limitations of Changing Antenna Polarization

While changing antenna polarization can bring several benefits, it also poses some challenges and limitations. One of the primary concerns is the potential for signal loss or degradation during the transition period. This can be mitigated by careful planning, testing, and implementation of the new polarization scheme. Additionally, receiver compatibility is a crucial factor, as some older radios may not be able to receive signals with the new polarization. Radio stations must therefore ensure that their listeners are informed and prepared for the change.
Technical Considerations for Changing Antenna Polarization
From a technical standpoint, changing antenna polarization requires careful consideration of several factors, including antenna design, transmitter power, and receiver sensitivity. The antenna must be designed to accommodate the new polarization scheme, and the transmitter power may need to be adjusted to ensure optimal signal strength. Receiver sensitivity is also critical, as it affects the ability of radios to detect and decode the signal. Signal processing techniques, such as equalization and diversity combining, can help mitigate the effects of polarization mismatch and improve overall signal quality.
- Antenna design: The antenna must be designed to accommodate the new polarization scheme, taking into account factors such as gain, beamwidth, and impedance matching.
- Transmitter power: The transmitter power may need to be adjusted to ensure optimal signal strength and coverage area.
- Receiver sensitivity: Receiver sensitivity is critical, as it affects the ability of radios to detect and decode the signal.
What are the benefits of changing antenna polarization for radio stations?
+The benefits of changing antenna polarization include improved signal-to-noise ratio, reduced multipath effects, and increased coverage area. Additionally, changing polarization can help reduce interference from other radio stations and provide a cleaner signal for listeners.
What are the challenges and limitations of changing antenna polarization?
+The challenges and limitations of changing antenna polarization include potential signal loss or degradation during the transition period, receiver compatibility issues, and the need for careful planning and testing to ensure a smooth transition.
In conclusion, changing antenna polarization can be a complex and challenging process for radio stations, but it also offers several benefits and opportunities for improvement. By carefully considering the technical and practical implications of polarization change, radio stations can optimize their signal quality, coverage area, and listener experience, ultimately providing better service to their audience.