Shear Stress Astronomy
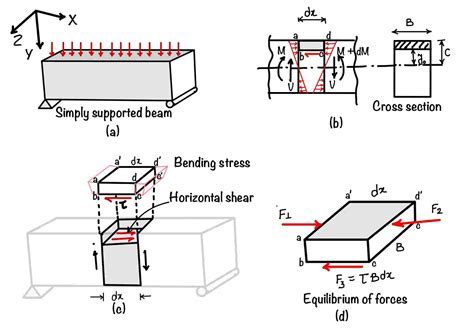
The study of shear stress in astronomy is a complex and fascinating field that has garnered significant attention in recent years. Shear stress, in the context of astronomy, refers to the stress that occurs when two adjacent layers of a fluid or a gas move past each other with different velocities. This phenomenon is particularly relevant in the study of celestial objects, such as galaxies, stars, and black holes, where the movement of matter and energy can lead to the generation of significant shear stresses. The understanding of shear stress in astronomy is crucial, as it can provide valuable insights into the behavior and evolution of celestial objects.
Shear Stress in Galactic Evolution

Galactic evolution is a complex process that involves the interaction of various physical mechanisms, including gravity, magnetic fields, and turbulence. Shear stress plays a significant role in this process, as it can influence the formation and evolution of galaxies. For instance, the shear stress generated by the differential rotation of a galaxy can lead to the formation of spiral arms, which are a characteristic feature of many galaxies. Additionally, shear stress can also affect the growth of supermassive black holes at the centers of galaxies, as it can regulate the accretion of material onto the black hole.
Shear Stress in Accretion Disks
Accretion disks are rotating disks of matter that surround compact objects, such as black holes and neutron stars. The viscosity of the disk, which is a measure of its resistance to shear stress, plays a crucial role in determining the behavior of the disk. The shear stress generated by the differential rotation of the disk can lead to the transfer of angular momentum and energy, which can affect the accretion rate and the overall evolution of the disk. The study of shear stress in accretion disks is essential for understanding the behavior of compact objects and the formation of jets and outflows.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Shear stress in a galactic disk | 10^(-12) - 10^(-10) Pa |
| Viscosity in an accretion disk | 10^(-4) - 10^(-2) kg/m/s |
| Angular momentum transfer rate | 10^(-3) - 10^(-1) kg/m^2/s |
Observational Evidence for Shear Stress
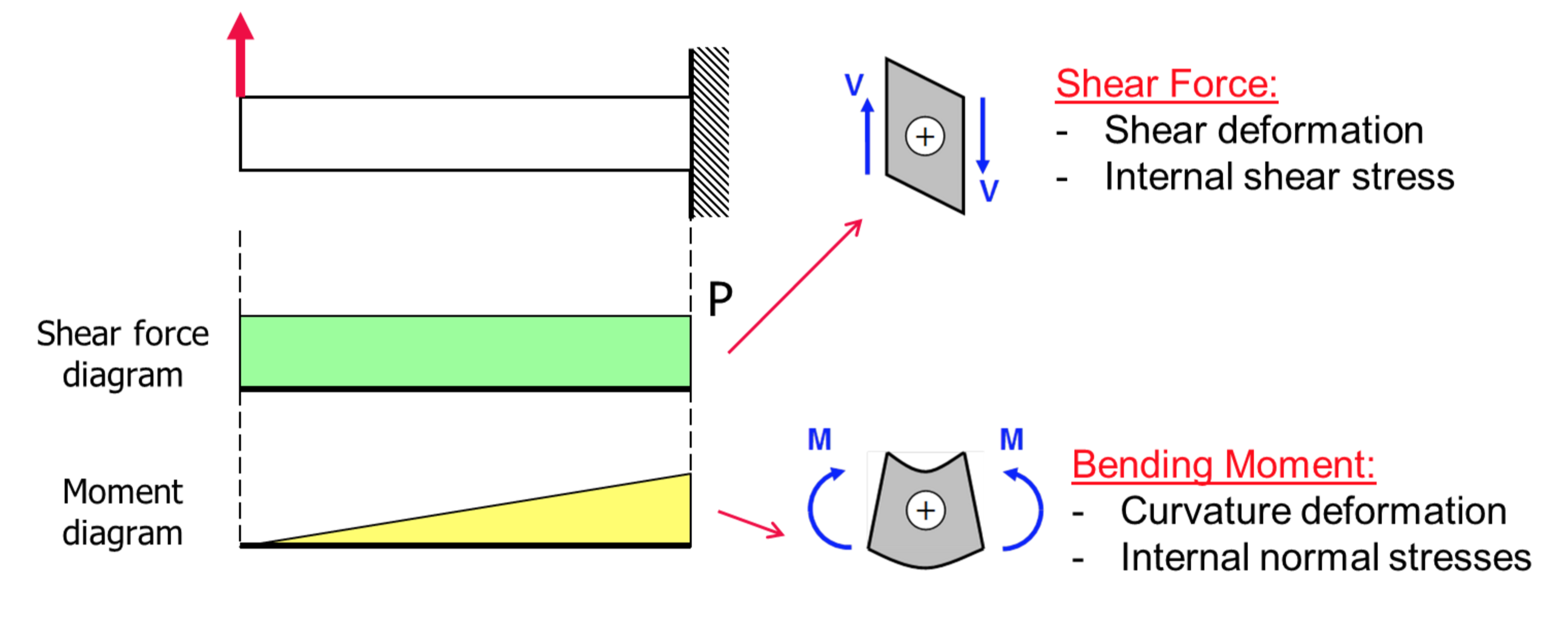
The observational evidence for shear stress in astronomy is based on a variety of observations, including the velocity distributions of galaxies and galaxy clusters, the morphology of accretion disks, and the polarization of radiation emitted by compact objects. For instance, the velocity distributions of galaxies and galaxy clusters can provide insights into the shear stress generated by the differential rotation of these systems. Additionally, the morphology of accretion disks can be affected by the shear stress generated by the differential rotation of the disk, which can lead to the formation of spiral arms and other features.
Simulations of Shear Stress
Numerical simulations play a crucial role in the study of shear stress in astronomy, as they can provide detailed insights into the behavior of complex systems. The hydrodynamic and magnetohydrodynamic simulations of galaxies and accretion disks can help to understand the generation and evolution of shear stress, and the impact of shear stress on the behavior of these systems. For instance, simulations of galaxy mergers can provide insights into the generation of shear stress and the formation of tidal tails and other features.
The simulations of shear stress in astronomy require the use of sophisticated numerical algorithms and high-performance computing facilities. The numerical methods used to simulate shear stress include the finite difference and finite element methods, which can provide accurate and efficient solutions to the equations of motion. The computational resources required to simulate shear stress include high-performance computing facilities, such as clusters and supercomputers, which can provide the necessary processing power and memory to simulate complex systems.
What is the role of shear stress in the formation of galaxies?
+The shear stress generated by the differential rotation of a galaxy can lead to the formation of spiral arms, which are a characteristic feature of many galaxies. Additionally, shear stress can also affect the growth of supermassive black holes at the centers of galaxies, as it can regulate the accretion of material onto the black hole.
How is shear stress simulated in numerical models of accretion disks?
+The simulations of shear stress in accretion disks require the use of sophisticated numerical algorithms and high-performance computing facilities. The numerical methods used to simulate shear stress include the finite difference and finite element methods, which can provide accurate and efficient solutions to the equations of motion.
In conclusion, the study of shear stress in astronomy is a complex and fascinating field that has garnered significant attention in recent years. The understanding of shear stress is essential for gaining insights into the behavior and evolution of celestial objects, and for making predictions about the formation and evolution of galaxies and galaxy clusters. The observational evidence for shear stress is based on a variety of observations, including the velocity distributions of galaxies and galaxy clusters, the morphology of accretion disks, and the polarization of radiation emitted by compact objects. The numerical simulations of shear stress play a crucial role in the study of this phenomenon, as they can provide detailed insights into the behavior of complex systems.