Structure Chitin Icon

The Structure Chitin Icon is a complex molecule that has garnered significant attention in the fields of biochemistry and materials science. Chitin, a long-chain polymer of a N-acetylglucosamine, is a primary component of the exoskeletons of arthropods, such as insects and crustaceans, as well as the cell walls of fungi. The unique structure of chitin, which is characterized by its rigid and flexible properties, makes it an ideal model for the development of novel biomimetic materials.
Chemical Structure of Chitin
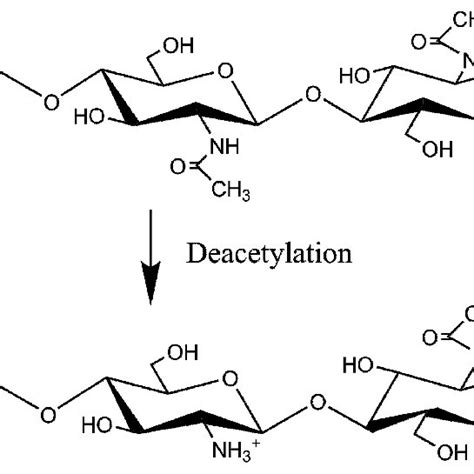
The chemical structure of chitin is composed of repeating units of N-acetylglucosamine, which are linked together through β-1,4-glycosidic bonds. This results in a long-chain polymer that is characterized by its high degree of crystallinity and rigidity. The hydrogen bonding between the N-acetylglucosamine units is responsible for the high tensile strength and stiffness of chitin, making it an ideal material for the development of novel biomimetic composites.
Physical Properties of Chitin
The physical properties of chitin are highly dependent on its degree of crystallinity and the presence of impurities. The crystallinity of chitin can be influenced by the method of preparation, with higher crystallinity resulting in increased rigidity and tensile strength. The moisture content of chitin can also have a significant impact on its physical properties, with higher moisture content resulting in decreased rigidity and tensile strength.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 150-200 MPa |
| Young's Modulus | 10-20 GPa |
| Crystallinity | 50-90% |

Biomimetic Applications of Chitin
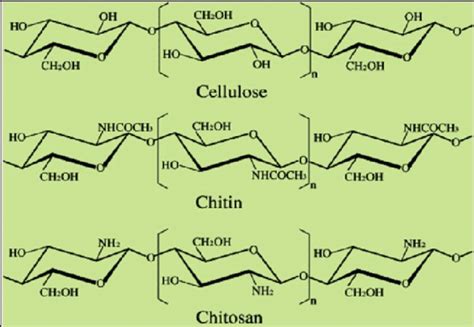
The biomimetic applications of chitin are highly diverse, with potential uses in the fields of tissue engineering, wound healing, and biodegradable packaging. The biocompatibility and biodegradability of chitin make it an ideal material for the development of novel biomedical devices, such as implantable scaffolds and wound dressings. The mechanical properties of chitin can also be tailored to mimic the properties of native tissues, making it an ideal material for the development of novel tissue engineering scaffolds.
Tissue Engineering Applications
The tissue engineering applications of chitin are highly promising, with potential uses in the development of novel implantable scaffolds and wound dressings. The porosity and pore size of chitin scaffolds can be tailored to mimic the properties of native tissues, making it an ideal material for the development of novel tissue engineering scaffolds. The biodegradability of chitin also makes it an ideal material for the development of novel biodegradable packaging materials.
- Tissue engineering scaffolds
- Wound dressings
- Biodegradable packaging materials
What are the potential applications of chitin in tissue engineering?
+The potential applications of chitin in tissue engineering are highly diverse, with potential uses in the development of novel implantable scaffolds and wound dressings. The biocompatibility and biodegradability of chitin make it an ideal material for the development of novel biomedical devices.
What are the physical properties of chitin that make it an ideal material for biomimetic applications?
+The physical properties of chitin that make it an ideal material for biomimetic applications include its high tensile strength, stiffness, and biodegradability. The crystallinity and moisture content of chitin can also be tailored to mimic the properties of native tissues.
In conclusion, the Structure Chitin Icon is a complex molecule with a unique structure and properties that make it an ideal material for biomimetic applications. The potential applications of chitin are highly diverse, with potential uses in the fields of tissue engineering, wound healing, and biodegradable packaging. Further research is needed to fully explore the potential of chitin and to develop novel biomimetic materials that can mimic the properties of native tissues.