Thc Synthesis Guide: Chemistry Made Easy
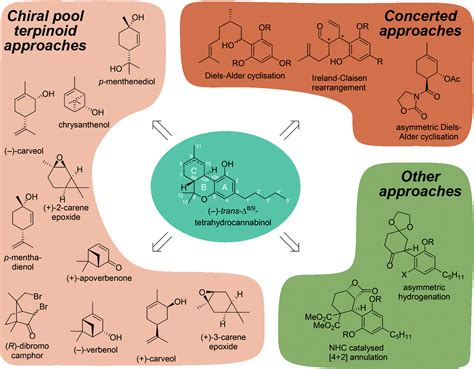
The synthesis of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive component of cannabis, is a complex process that requires a deep understanding of organic chemistry. THC is a cannabinoid, a class of compounds found in the cannabis plant, and its synthesis has been a subject of interest for both medicinal and recreational purposes. In this guide, we will delve into the chemistry behind THC synthesis, exploring the various methods, reagents, and conditions required to produce this compound.
Introduction to THC Synthesis

THC synthesis involves the combination of several chemical precursors, which undergo a series of reactions to form the desired compound. The most common method of THC synthesis is through the use of cannabinolic acid, a precursor found in the cannabis plant. However, this method can be time-consuming and requires large quantities of plant material. Alternatively, chemists can synthesize THC from olivetolic acid and geranyl pyrophosphate, two compounds that are readily available and can be easily synthesized.
Chemical Precursors and Reagents
The synthesis of THC requires several chemical precursors and reagents, including:
- Olivetolic acid
- Geranyl pyrophosphate
- Sodium hydroxide
- Hydrochloric acid
- Acetic anhydride
These reagents must be handled with care, as they can be hazardous if not used properly. It is essential to follow proper safety protocols and use personal protective equipment when working with these chemicals.
| Reagent | Function |
|---|---|
| Olivetolic acid | Provides the core structure of THC |
| Geranyl pyrophosphate | Provides the side chain of THC |
| Sodium hydroxide | Used for hydrolysis and purification |
| Hydrochloric acid | Used for acidification and purification |
| Acetic anhydride | Used for acetylation and purification |

Step-by-Step Synthesis of THC
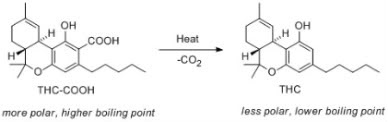
The synthesis of THC involves several steps, including the formation of the core structure, the addition of the side chain, and the purification of the final product. The following is a step-by-step guide to the synthesis of THC:
- Formation of the core structure: Olivetolic acid is converted into the core structure of THC through a series of reactions, including hydrolysis and decarboxylation.
- Addition of the side chain: Geranyl pyrophosphate is added to the core structure to form the side chain of THC.
- Purification: The resulting compound is purified through a series of reactions, including acidification, hydrolysis, and acetylation.
Challenges and Limitations
The synthesis of THC is a challenging process that requires careful attention to detail and a deep understanding of organic chemistry. Some of the challenges and limitations of THC synthesis include:
- Low yields: The synthesis of THC can result in low yields, making it necessary to repeat the process multiple times to obtain the desired amount of compound.
- Impurities: The synthesis of THC can result in the formation of impurities, which must be removed through purification steps.
- Regulatory issues: The synthesis of THC is regulated by law in many countries, making it essential to ensure that all synthesis activities are conducted in compliance with local regulations.
What is the most common method of THC synthesis?
+The most common method of THC synthesis is through the use of cannabinolic acid, a precursor found in the cannabis plant. However, this method can be time-consuming and requires large quantities of plant material.
What are the challenges and limitations of THC synthesis?
+The synthesis of THC is a challenging process that requires careful attention to detail and a deep understanding of organic chemistry. Some of the challenges and limitations of THC synthesis include low yields, impurities, and regulatory issues.
In conclusion, the synthesis of THC is a complex process that requires a deep understanding of organic chemistry and proper laboratory techniques. While there are challenges and limitations to THC synthesis, the development of new methods and technologies has made it possible to produce high-quality THC for medicinal and recreational purposes. It is essential to ensure that all synthesis activities are conducted in compliance with local regulations and to follow proper safety protocols when working with hazardous chemicals.