Time Gain Compensation
The concept of Time Gain Compensation (TGC) is a crucial aspect of ultrasound technology, particularly in the field of medical imaging. TGC refers to the process of adjusting the amplitude of ultrasound signals in real-time to compensate for the attenuation of sound waves as they travel through tissues. This compensation is essential to ensure that the resulting images are of high quality and provide accurate diagnostic information. The principle behind TGC is based on the fact that different tissues absorb and scatter sound waves to varying degrees, leading to a loss of signal intensity with depth.
Principle of Time Gain Compensation
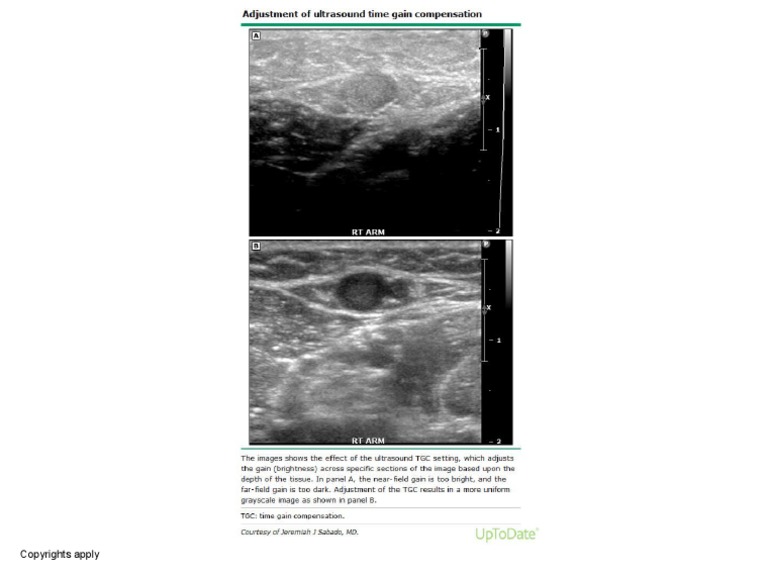
The TGC system operates by applying a time-varying gain to the received ultrasound signals. The gain increases with time to counteract the attenuation of the sound waves. This process involves the use of a variable gain amplifier that adjusts the signal amplitude based on the time elapsed since the transmission of the ultrasound pulse. The amplifier’s gain setting is controlled by a time-varying function, which is typically predefined and stored in the ultrasound system’s memory. By applying this time-varying gain, the TGC system ensures that the signal amplitudes from different tissue depths are comparable, resulting in a more uniform image.
Implementation of Time Gain Compensation
The implementation of TGC involves several key components, including the ultrasound transducer, the pulse generator, and the signal processing unit. The ultrasound transducer converts electrical signals into sound waves and vice versa, while the pulse generator produces the high-frequency electrical pulses that drive the transducer. The signal processing unit, which includes the TGC system, processes the received signals to produce the final image. The TGC system is typically implemented using a combination of analog and digital circuitry, with the analog components handling the initial signal amplification and the digital components providing the time-varying gain control.
| TGC Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Ultrasound Transducer | Converts electrical signals into sound waves and vice versa |
| Pulse Generator | Produces high-frequency electrical pulses to drive the transducer |
| Signal Processing Unit | Processes received signals to produce the final image |
Types of Time Gain Compensation

There are several types of TGC systems, including linear TGC, non-linear TGC, and adaptive TGC. Linear TGC applies a constant rate of gain increase with time, while non-linear TGC uses a more complex function to adjust the gain. Adaptive TGC, on the other hand, uses real-time feedback to adjust the gain setting based on the received signal amplitude. Each type of TGC has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of TGC system depends on the specific application and the type of tissue being imaged.
Applications of Time Gain Compensation
TGC has a wide range of applications in medical imaging, including obstetric ultrasound, cardiovascular ultrasound, and musculoskeletal ultrasound. In obstetric ultrasound, TGC is used to produce high-quality images of the fetus and placenta, while in cardiovascular ultrasound, it is used to image the heart and blood vessels. In musculoskeletal ultrasound, TGC is used to image muscles, tendons, and ligaments. The use of TGC in these applications enables the production of high-quality images that provide accurate diagnostic information and facilitate effective treatment planning.
- Obstetric Ultrasound: TGC is used to produce high-quality images of the fetus and placenta
- Cardiovascular Ultrasound: TGC is used to image the heart and blood vessels
- Musculoskeletal Ultrasound: TGC is used to image muscles, tendons, and ligaments
What is the primary function of Time Gain Compensation in ultrasound imaging?
+The primary function of Time Gain Compensation (TGC) in ultrasound imaging is to adjust the amplitude of ultrasound signals in real-time to compensate for the attenuation of sound waves as they travel through tissues. This compensation is essential to ensure that the resulting images are of high quality and provide accurate diagnostic information.
What are the different types of Time Gain Compensation systems?
+There are several types of Time Gain Compensation (TGC) systems, including linear TGC, non-linear TGC, and adaptive TGC. Linear TGC applies a constant rate of gain increase with time, while non-linear TGC uses a more complex function to adjust the gain. Adaptive TGC, on the other hand, uses real-time feedback to adjust the gain setting based on the received signal amplitude.
In conclusion, Time Gain Compensation is a critical component of ultrasound imaging technology, enabling the production of high-quality images that provide accurate diagnostic information. The TGC system compensates for the attenuation of sound waves as they travel through tissues, ensuring that the resulting images are uniform and of high quality. With its wide range of applications in medical imaging, TGC continues to play a vital role in the diagnosis and treatment of a wide range of medical conditions.

