Transformer Machine Learning Test List

The Transformer architecture has revolutionized the field of natural language processing (NLP) and beyond, offering unprecedented capabilities in handling sequential data. Introduced in the paper "Attention Is All You Need" by Vaswani et al. in 2017, the Transformer model has been widely adopted and further developed for various machine learning tasks. This comprehensive overview will delve into the specifics of the Transformer architecture, its applications, and the current state of research in this domain.
Introduction to Transformer Architecture
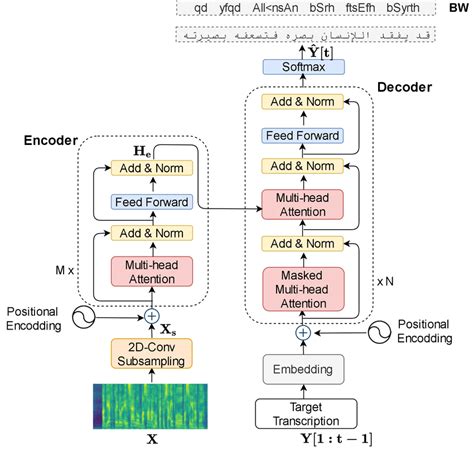
The Transformer model is based on self-attention mechanisms, allowing it to weigh the importance of different parts of the input data relative to each other. This is particularly useful in NLP tasks where understanding the context and relationships between different words or tokens is crucial. Unlike traditional recurrent neural networks (RNNs) that process sequences sequentially, the Transformer can process all parts of the input simultaneously, making it more efficient for parallelization and significantly speeding up training times.
Key Components of the Transformer
The Transformer consists of an encoder and a decoder. The encoder takes in a sequence of tokens (e.g., words or characters) and outputs a sequence of vectors. The decoder then generates output tokens one at a time, based on the encoder’s output. Self-attention is a critical mechanism within both the encoder and decoder, allowing the model to attend to all positions in the input sequence simultaneously and weigh their importance. Additionally, the Transformer uses position encoding to preserve the order of the sequence, as it does not inherently capture this information like RNNs do.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Encoder | Takes input sequence and outputs a vector sequence |
| Decoder | Generates output sequence based on encoder output |
| Self-Attention | Allows the model to weigh importance of different input parts |
| Position Encoding | Preserves sequence order information |
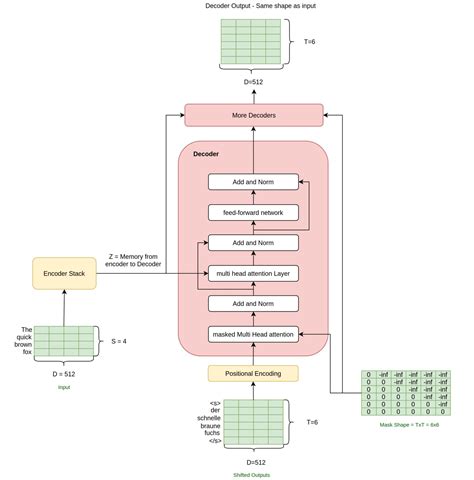
Applications of the Transformer
The Transformer has found applications in a wide range of NLP tasks, including but not limited to machine translation, text summarization, question answering, and text generation. Its success in these areas has led to the development of more specialized variants, such as BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers), RoBERTa, and XLNet, which have achieved state-of-the-art results in various benchmarks.
Machine Translation
Machine translation is one of the earliest applications of the Transformer. By leveraging its ability to capture complex contextual relationships, the Transformer has significantly improved the quality of machine translation, making it more accurate and fluent. Parallelization is another advantage, allowing for faster training of large-scale translation models.
- Improved accuracy over traditional sequence-to-sequence models
- Faster training times due to parallelization
- Ability to handle low-resource languages
Future Implications and Challenges
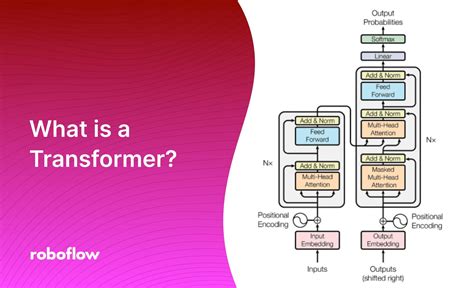
Despite the significant advancements brought about by the Transformer, there are challenges and future directions to explore. One of the major challenges is the computational cost associated with training large Transformer models, which requires substantial computational resources and data. Additionally, there is a growing need to develop more explainable and transparent models, as the complexity of deep learning architectures like the Transformer can make it difficult to understand their decision-making processes.
- Developing more efficient training methods
- Improving model interpretability
- Applying Transformers to multimodal tasks
What are the primary advantages of the Transformer architecture?
+The primary advantages include its ability to handle parallelization, capture long-range dependencies, and weigh the importance of different parts of the input data through self-attention. This makes it particularly effective for tasks that require deep understanding of complex relationships within sequential data.
How does the Transformer architecture improve upon traditional RNNs?
+The Transformer improves upon RNNs by allowing for parallel processing of the input sequence, reducing the impact of vanishing gradients, and more effectively capturing long-range dependencies through its self-attention mechanism. This results in faster training times and improved performance on many NLP tasks.
In conclusion, the Transformer architecture has significantly impacted the field of machine learning, particularly in NLP. Its innovative use of self-attention and parallelization has opened up new avenues for research and application, from machine translation and text generation to multimodal processing and beyond. As research continues to evolve, addressing the challenges associated with the Transformer, such as computational efficiency and model interpretability, will be crucial for unlocking its full potential and exploring new frontiers in AI.
