Us Mexico Border Guide: Regions Explained

The US-Mexico border stretches for approximately 1,954 miles (3,145 kilometers), dividing the United States and Mexico. This extensive border is not just a physical barrier but also a cultural, economic, and environmental divide. Understanding the different regions along the border is crucial for grasping the complexities of the US-Mexico relationship, immigration policies, and the daily lives of people living in these areas. The border regions are diverse, each with its unique characteristics, challenges, and opportunities.
Introduction to US-Mexico Border Regions

The US-Mexico border can be broadly divided into several regions, each with distinct geographical features, urban centers, and socio-economic conditions. From the Pacific Ocean to the Gulf of Mexico, the border traverses through deserts, mountains, and rivers, creating a variety of landscapes and ecosystems. The main regions include the California Border Region, the Arizona Border Region, the New Mexico Border Region, the Texas Border Region, and the Rio Grande Valley. Each of these regions has its own set of challenges and opportunities, ranging from immigration and border security to economic development and environmental conservation.
California Border Region
The California Border Region is the westernmost part of the US-Mexico border, stretching from the Pacific Ocean to the Colorado River. This region includes the San Ysidro Port of Entry, one of the busiest border crossings in the world, and the city of Tijuana, a major urban center in Mexico. The California border is characterized by its rugged terrain, with mountains and deserts dominating the landscape. The region is also home to several important ecological areas, including the Sonoran Desert and the Pacific Coast. Economically, the region is significant for both the US and Mexico, with trade, tourism, and agriculture being major contributors. The maquiladora industry, which involves the assembly and manufacture of goods in Mexico for export to the US, is particularly prominent in this region.
| Region | Population (US Side) | Main Cities |
|---|---|---|
| California Border Region | Approximately 5 million | San Diego, Imperial |
| Arizona Border Region | Approximately 2 million | Tucson, Yuma |
| New Mexico Border Region | Approximately 1 million | Las Cruces, Deming |
| Texas Border Region | Approximately 5.5 million | El Paso, Laredo, Brownsville |

Arizona Border Region
The Arizona Border Region is known for its harsh desert landscape and significant Native American reservations. The region includes the Tohono O’odham Nation, which has its own distinct cultural and linguistic heritage. Border security is a major concern in this region due to its remote areas and the presence of drug trafficking routes. However, the region is also rich in natural resources and has potential for solar and wind energy development. The city of Nogales, both in Arizona and Mexico, is an important commercial center, with trade in goods such as produce and manufacturing materials being significant.
New Mexico Border Region
New Mexico’s border with Mexico is relatively short compared to other states but is historically and culturally significant. The region includes the cities of Las Cruces and Deming, which have strong agricultural sectors. The Rio Grande River forms the border in this region, posing challenges for water management and conservation. The region is also home to several important historical sites, reflecting the complex and often contentious history of the US-Mexico border. Economically, the region benefits from its proximity to major transportation routes and its role in international trade.
Texas Border Region
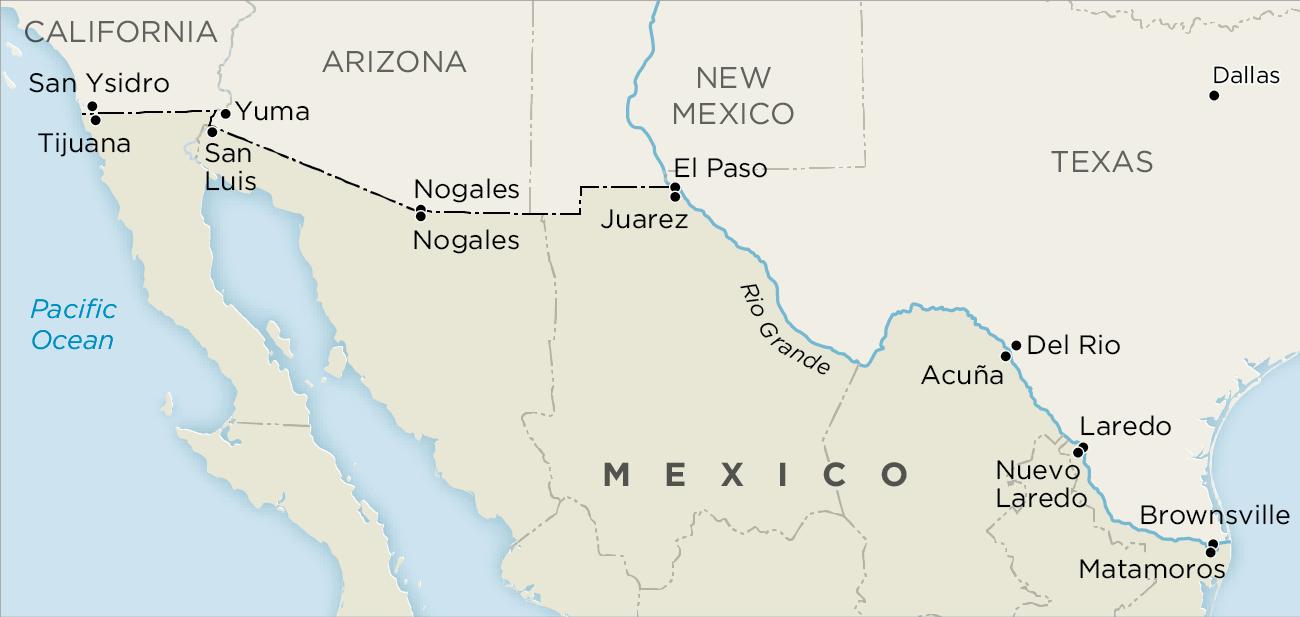
The Texas Border Region is the longest and most populous part of the US-Mexico border, stretching from El Paso to Brownsville. This region includes several major urban centers on both sides of the border, such as El Paso and Ciudad Juárez, and Laredo and Nuevo Laredo. The Rio Grande Valley in southern Texas is a significant agricultural producer and has a diverse economy that includes healthcare, education, and tourism. Immigration and border security are critical issues in this region, with the Rio Grande posing both a physical and symbolic barrier between the US and Mexico. The region is also rich in cultural heritage, with a unique blend of Mexican and American influences.
What are the main challenges faced by the US-Mexico border regions?
+The US-Mexico border regions face several challenges, including immigration and border security, economic development, environmental conservation, and the impact of drug trafficking. Each region has its unique set of challenges and opportunities, influenced by its geographical characteristics, economic conditions, and cultural context.
How do the different regions along the US-Mexico border contribute to the bilateral relationship between the US and Mexico?
+The regions along the US-Mexico border play a crucial role in the bilateral relationship, contributing to trade, cultural exchange, and economic cooperation. Each region has its own strengths and weaknesses, and understanding these regional dynamics is essential for developing effective policies that promote mutual benefit and cooperation.
In conclusion, the US-Mexico border is a complex and multifaceted entity, with different regions presenting unique challenges and opportunities. Understanding these regions is crucial for addressing the issues that arise along the border, from immigration and security to economic development and environmental protection. By recognizing the diversity and richness of the border regions, policymakers and stakeholders can work towards creating more effective and sustainable solutions that benefit both the US and Mexico.
