Us Mexico Map: Border Details
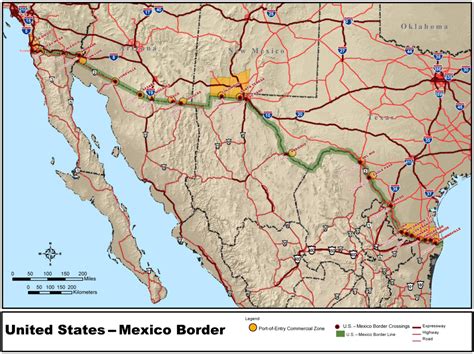
The US-Mexico border is one of the most extensive and complex international borders in the world, stretching approximately 1,954 miles (3,145 kilometers) from the Pacific Ocean to the Gulf of Mexico. This border separates the United States from Mexico and is a significant geographical and political divide between the two countries. Understanding the details of this border is crucial for various reasons, including trade, immigration, and national security.
Geographical Overview

The US-Mexico border traverses diverse landscapes, including deserts, mountains, and rivers. The border starts at the Pacific Ocean, where the states of California (US) and Baja California (Mexico) meet. It then moves eastward, passing through the states of Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas in the US, and the states of Sonora, Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo León, and Tamaulipas in Mexico. The border ends at the Gulf of Mexico, where the states of Texas (US) and Tamaulipas (Mexico) converge.
Border Crossings and Ports of Entry
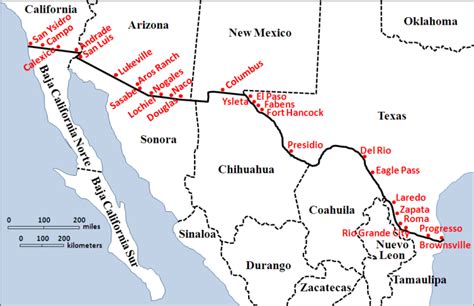
There are numerous border crossings and ports of entry along the US-Mexico border, which facilitate the movement of people, goods, and services between the two countries. Some of the busiest border crossings include:
- San Ysidro Port of Entry, California: One of the busiest land border crossings in the world, with over 50,000 vehicles and 25,000 pedestrians crossing daily.
- El Paso-Ciudad Juárez Border Crossing, Texas/Chihuahua: A major commercial and tourist crossing, with significant trade and cultural exchange between the two cities.
- Laredo-Nuevo Laredo Border Crossing, Texas/Tamaulipas: A critical crossing for trade, with a large volume of goods transported by truck and rail.
| Border Crossing | Location | Volume of Traffic |
|---|---|---|
| San Ysidro | California/Baja California | 50,000+ vehicles, 25,000+ pedestrians daily |
| El Paso-Ciudad Juárez | Texas/Chihuahua | 20,000+ vehicles, 10,000+ pedestrians daily |
| Laredo-Nuevo Laredo | Texas/Tamaulipas | 15,000+ vehicles, 5,000+ pedestrians daily |

Border Security and Management
The US-Mexico border is managed by various agencies, including US Customs and Border Protection (CBP), US Border Patrol, and the Mexican government’s immigration and customs agencies. These agencies work to prevent illegal crossings, smuggling, and other criminal activities while facilitating legitimate trade and travel.
Infrastructure and Technology
The US-Mexico border features a range of infrastructure and technology to support border management, including:
- Physical barriers: Fences, walls, and other barriers to prevent unauthorized crossings.
- Sensors and surveillance systems: Cameras, radar, and other technologies to detect and track border activity.
- Checkpoints and inspection stations: Facilities to inspect vehicles and cargo for contraband and to process legitimate trade and travel.
These infrastructure and technology investments aim to enhance border security while facilitating the efficient movement of people and goods.
What is the total length of the US-Mexico border?
+The US-Mexico border is approximately 1,954 miles (3,145 kilometers) long.
Which US-Mexico border crossing is the busiest?
+The San Ysidro Port of Entry in California is one of the busiest land border crossings in the world, with over 50,000 vehicles and 25,000 pedestrians crossing daily.
In conclusion, the US-Mexico border is a complex and dynamic region, with significant implications for trade, immigration, and national security. Understanding the geographical, economic, and cultural context of this border is essential for effective management and cooperation between the two countries.
