What Are Emotions Vs Feelings? Google Scholar Insights

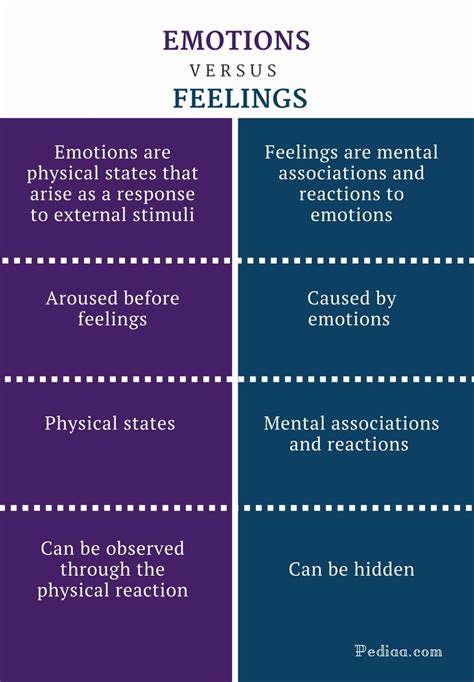
Emotions and feelings are two closely related yet distinct concepts that have been extensively studied in the fields of psychology, neuroscience, and philosophy. While often used interchangeably, emotions and feelings have different underlying mechanisms, functions, and implications for human behavior and well-being. According to Google Scholar insights, research in this area has led to a deeper understanding of the complex relationships between emotions, feelings, and cognitive processes.
Defining Emotions and Feelings

Emotions are typically defined as complex psychological and physiological states that arise in response to specific stimuli or situations. Emotions are often characterized by distinct patterns of brain activity, hormonal changes, and expressive behaviors, such as facial expressions, body language, and vocal tone. Affective neuroscience has identified specific brain regions and networks involved in emotional processing, including the amygdala, prefrontal cortex, and anterior cingulate cortex. Emotions can be categorized into primary emotions, such as happiness, sadness, fear, and anger, which are universally experienced across cultures.
In contrast, feelings are subjective, introspective experiences that arise from the interpretation and evaluation of emotions. Feelings are often described as the conscious awareness of emotional states, which can be influenced by cognitive appraisals, personal values, and past experiences. Feelings can be thought of as the "what it's like" aspect of emotions, providing a sense of pleasure, displeasure, or indifference. Phenomenology, a philosophical approach, emphasizes the importance of subjective experience and the lived quality of feelings.
Key Differences Between Emotions and Feelings
A key distinction between emotions and feelings lies in their duration and intensity. Emotions are typically short-lived and intense, whereas feelings can be more prolonged and nuanced. For example, the emotion of fear may be triggered by a sudden threat, whereas the feeling of anxiety may persist long after the initial threat has passed. Additionally, emotions tend to be more automatic and universal, whereas feelings are more context-dependent and culturally relative.
Another important difference concerns the role of cognition in emotions and feelings. Emotions can occur without conscious awareness or cognitive appraisal, whereas feelings often involve a degree of cognitive processing and evaluation. This is reflected in the concept of emotional regulation, which refers to the ability to manage and modulate emotional responses through cognitive strategies, such as reappraisal or suppression.
| Characteristics | Emotions | Feelings |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Short-lived | Prolonged |
| Intensity | Intense | Nuanced |
| Cognition | Automatic | Cognitively mediated |
| Cultural relativity | Universal | Culturally relative |

Neural Mechanisms Underlying Emotions and Feelings
Recent advances in neuroimaging and neurophysiology have shed light on the neural mechanisms underlying emotions and feelings. The amygdala, a small almond-shaped structure in the temporal lobe, plays a critical role in the processing of emotional stimuli, particularly fear and anxiety. The pre-frontal cortex, responsible for executive function and decision-making, is also involved in the regulation of emotions and the generation of feelings.
Furthermore, research on neuroplasticity has shown that the brain's emotional systems are highly adaptable and can be shaped by experience, learning, and environment. This has significant implications for the development of novel therapeutic approaches, such as mindfulness-based interventions, which aim to modify emotional processing and promote emotional well-being.
Implications for Mental Health and Well-being
The distinction between emotions and feelings has important implications for our understanding of mental health and well-being. Emotional dysregulation, characterized by difficulties in managing and modulating emotional responses, is a common feature of many mental health disorders, including anxiety, depression, and borderline personality disorder. By recognizing the complex interplay between emotions and feelings, clinicians can develop more effective therapeutic strategies, such as emotion-focused therapy, which aims to enhance emotional awareness, regulation, and expression.
In addition, research on emotions and feelings has significant implications for our understanding of social relationships and decision-making processes. Emotions and feelings play a critical role in shaping our social interactions, influencing our attitudes towards others, and guiding our decision-making. By recognizing the importance of emotions and feelings in these contexts, we can develop more effective strategies for building and maintaining healthy relationships, as well as making informed, emotionally intelligent decisions.
What is the main difference between emotions and feelings?
+The main difference between emotions and feelings lies in their duration, intensity, and cognitive mediation. Emotions are typically short-lived and intense, whereas feelings are more prolonged and nuanced. Emotions can occur without conscious awareness or cognitive appraisal, whereas feelings often involve a degree of cognitive processing and evaluation.
How do emotions and feelings relate to mental health and well-being?
+Emotions and feelings play a critical role in mental health and well-being. Emotional dysregulation, characterized by difficulties in managing and modulating emotional responses, is a common feature of many mental health disorders. By recognizing the complex interplay between emotions and feelings, clinicians can develop more effective therapeutic strategies, such as emotion-focused therapy, which aims to enhance emotional awareness, regulation, and expression.
In conclusion, the distinction between emotions and feelings is a complex and multifaceted issue that has important implications for our understanding of human behavior, mental health, and well-being. By recognizing the unique characteristics and functions of emotions and feelings, we can develop more effective strategies for emotional regulation, empathy, and decision-making, ultimately promoting greater well-being and life satisfaction.
