Yale Climate Opinion Map
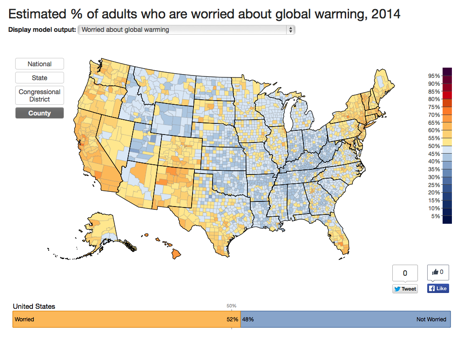
The Yale Climate Opinion Map is a comprehensive tool designed to visualize and understand public perceptions and opinions on climate change across the United States. Developed by the Yale Program on Climate Change Communication, this map provides detailed insights into the geographic distribution of climate change beliefs, risk perceptions, and policy support at the state, congressional district, and county levels. The data is based on a large-scale survey of Americans, making it one of the most accurate and detailed representations of climate change opinions in the country.
Methodology and Data Collection

The Yale Climate Opinion Map is constructed using a statistical model that combines data from a national survey with demographic and geographic data. The model estimates public opinion on climate change for each geographic area, including states, congressional districts, and counties. The survey, which forms the basis of the map, asks respondents about their beliefs regarding the existence and causes of climate change, their perceptions of the risks associated with it, and their support for various climate policies. By integrating these responses with demographic data, such as age, education level, and political affiliation, the researchers can provide a nuanced understanding of how climate opinions vary across different regions and populations.
Key Findings and Trends
One of the key findings from the Yale Climate Opinion Map is the significant variation in public opinion on climate change across different parts of the United States. While there are areas where a strong majority of residents believe in the reality of human-caused climate change and support policies to address it, there are also regions where skepticism about climate change is more prevalent. For instance, coastal areas and regions with a high incidence of climate-related disasters tend to have higher levels of concern and support for climate action. In contrast, some inland and rural areas exhibit lower levels of climate change belief and policy support. These trends highlight the importance of considering geographic and demographic factors in climate communication and policy strategies.
| Region | % Believing in Human-Caused Climate Change | % Supporting Climate Policies |
|---|---|---|
| Northeast | 73% | 62% |
| West Coast | 75% | 65% |
| Southern States | 58% | 45% |
| Midwest | 61% | 50% |

Implications for Climate Policy and Communication

The insights provided by the Yale Climate Opinion Map have significant implications for the development and implementation of climate policies. By understanding where there is strong public support for climate action, policymakers can identify opportunities to enact policies that reflect the will of their constituents. Conversely, areas with lower levels of support may require more targeted education and outreach efforts to build a broader consensus for climate action. The map also highlights the importance of considering the local and regional impacts of climate change in policy discussions, as these factors can significantly influence public perceptions and support for climate policies.
Future Research Directions
Future research directions for the Yale Climate Opinion Map could include expanding the scope of the survey to cover additional aspects of climate change opinion, such as specific policy preferences or the role of climate change in voting decisions. Additionally, integrating the map with other datasets, such as economic or health outcomes related to climate change, could provide even deeper insights into the complex relationships between public opinion, policy, and the impacts of climate change. Longitudinal studies could also track changes in public opinion over time, helping to identify effective strategies for shifting public perceptions and building support for climate action.
- Expanding survey questions to cover more specific climate policies and personal behaviors.
- Integrating with economic and health datasets to understand the multidimensional impacts of climate change.
- Conducting longitudinal studies to track changes in public opinion and the effectiveness of communication strategies.
What is the purpose of the Yale Climate Opinion Map?
+The Yale Climate Opinion Map is designed to provide a detailed understanding of public opinions and beliefs about climate change across the United States, aiding in the development of effective communication and policy strategies.
How is the data for the map collected?
+The data is collected through a national survey that asks respondents about their beliefs and perceptions regarding climate change, combined with demographic and geographic data to estimate opinions at the state, congressional district, and county levels.
What are some key findings from the Yale Climate Opinion Map?
+Key findings include significant geographic variation in climate change beliefs and policy support, with higher concern and support in coastal areas and regions experiencing climate-related disasters, and lower levels in some inland and rural areas.