Retrieval Psychology Explained

Retrieval psychology is a branch of cognitive psychology that focuses on the process of retrieving information from memory. It is a crucial aspect of learning and memory, as it enables individuals to recall previously learned information and apply it to new situations. The study of retrieval psychology has led to a deeper understanding of how memory works and has significant implications for education, training, and cognitive development. In this article, we will delve into the principles of retrieval psychology, its underlying mechanisms, and its applications in various fields.
Introduction to Retrieval Psychology
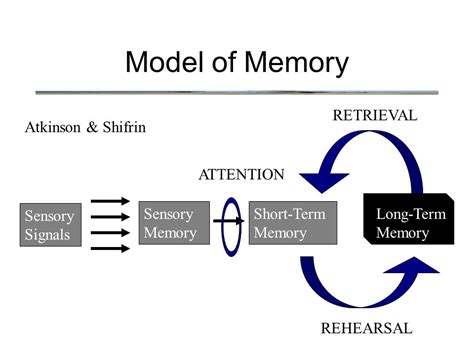
Retrieval psychology is based on the idea that the act of retrieving information from memory strengthens the memory itself, making it easier to recall in the future. This concept is often referred to as the testing effect, which states that the process of retrieving information from memory is more effective for learning and retention than simply re-reading or re-studying the material. The testing effect has been consistently demonstrated in numerous studies, showing that retrieval practice can improve memory recall, reduce forgetting, and promote long-term retention.
Key factors that influence the effectiveness of retrieval psychology include the type of retrieval practice, the timing of retrieval, and the level of difficulty. For example, spaced repetition has been shown to be an effective technique for promoting long-term retention, as it involves reviewing material at increasingly longer intervals to help solidify it in memory. Additionally, retrieval practice with feedback has been found to be more effective than retrieval practice without feedback, as it provides individuals with an opportunity to correct their mistakes and reinforce their understanding of the material.
Underlying Mechanisms of Retrieval Psychology
The underlying mechanisms of retrieval psychology involve the interaction between different cognitive processes, including attention, perception, and memory. When individuals engage in retrieval practice, they must actively recall the information from memory, which requires the coordination of multiple cognitive systems. This process involves the reconsolidation of memory, which refers to the re-stabilization of previously consolidated memories. Reconsolidation is thought to occur through the process of neural replay, where the brain reactivates the neural pathways that were originally involved in the encoding of the memory.
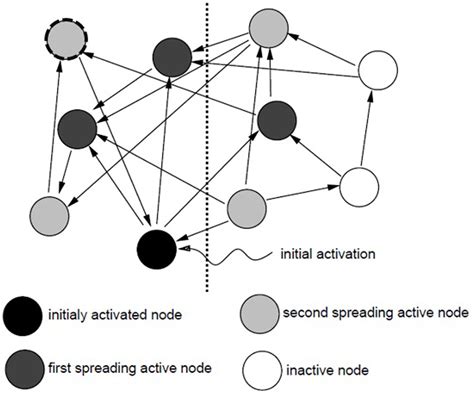
A key aspect of retrieval psychology is the concept of retrieval-induced forgetting, which refers to the phenomenon where the retrieval of one piece of information can lead to the forgetting of other, related information. This occurs because the act of retrieval can strengthen the memory of the retrieved information, making it more competitive with other, related memories. As a result, the non-retrieved information may become less accessible and more susceptible to forgetting.
| Retrieval Technique | Effectiveness |
|---|---|
| Spaced repetition | High |
| Retrieval practice with feedback | High |
| Massed practice | Low |
Applications of Retrieval Psychology

Retrieval psychology has significant implications for education, training, and cognitive development. In educational settings, retrieval practice can be used to improve student learning and retention, particularly in subjects that require the recall of large amounts of factual information. For example, flashcards can be used to promote the retrieval of key terms and concepts, while quizzes and tests can be used to promote the retrieval of more complex information.
In training settings, retrieval practice can be used to improve the development of skills and knowledge, particularly in fields that require the recall of procedural information. For example, simulation-based training can be used to promote the retrieval of critical skills, such as those required in emergency response situations. Additionally, virtual reality training can be used to promote the retrieval of complex skills, such as those required in surgical procedures.
Future Implications of Retrieval Psychology
The study of retrieval psychology has significant implications for our understanding of human cognition and behavior. As our understanding of the underlying mechanisms of retrieval psychology continues to grow, we can expect to see the development of more effective techniques for promoting learning and retention. For example, personalized learning systems can be designed to optimize the retrieval of information based on an individual’s learning style and abilities. Additionally, neurofeedback training can be used to promote the development of cognitive skills, such as attention and working memory.
A key area of future research in retrieval psychology is the development of retrieval-based interventions for individuals with cognitive impairments, such as those with Alzheimer’s disease or traumatic brain injury. These interventions can be designed to promote the retrieval of information and skills, with the goal of improving cognitive function and promoting independence.
What is the testing effect in retrieval psychology?
+The testing effect refers to the phenomenon where the act of retrieving information from memory strengthens the memory itself, making it easier to recall in the future. This effect has been consistently demonstrated in numerous studies, showing that retrieval practice can improve memory recall, reduce forgetting, and promote long-term retention.
What is retrieval-induced forgetting in retrieval psychology?
+Retrieval-induced forgetting refers to the phenomenon where the retrieval of one piece of information can lead to the forgetting of other, related information. This occurs because the act of retrieval can strengthen the memory of the retrieved information, making it more competitive with other, related memories.
In conclusion, retrieval psychology is a complex and multifaceted field that has significant implications for our understanding of human cognition and behavior. By understanding the principles of retrieval psychology, we can develop more effective techniques for promoting learning and retention, and improve our ability to recall information and skills in a wide range of contexts.

